SQL Console (Milvus)
NineData SQL Console supports Milvus vector databases by encapsulating industry-standard MySQL syntax, providing SQL extension capabilities for vector databases. Developers do not need to learn specific APIs and can directly use familiar SQL syntax to implement vector data management, similarity searches, and other operations, significantly reducing the technical barrier.
Background Information
Milvus is an open-source vector database developed by Zilliz, designed to solve the challenges of unstructured data processing in the era of artificial intelligence. Milvus, as a new generation of infrastructure for AI applications, is widely used in scenarios such as AI inference and semantic search.
Although Milvus has strong technical capabilities, its native interface has a significant learning curve. NineData addresses the pain points of using Milvus by encapsulating MySQL syntax, allowing developers to directly use familiar SQL syntax to implement all the features of Milvus.
Prerequisites
The target database to be managed has been added to NineData. For instructions on how to add, please refer to Manage Data Sources. Milvus versions are 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, and the instance type is Alibaba Cloud managed Milvus.
In the organizational mode (), you must have read-only, DML, or DDL permissions for the target data source.
tipRead-only permissions only support query operations.
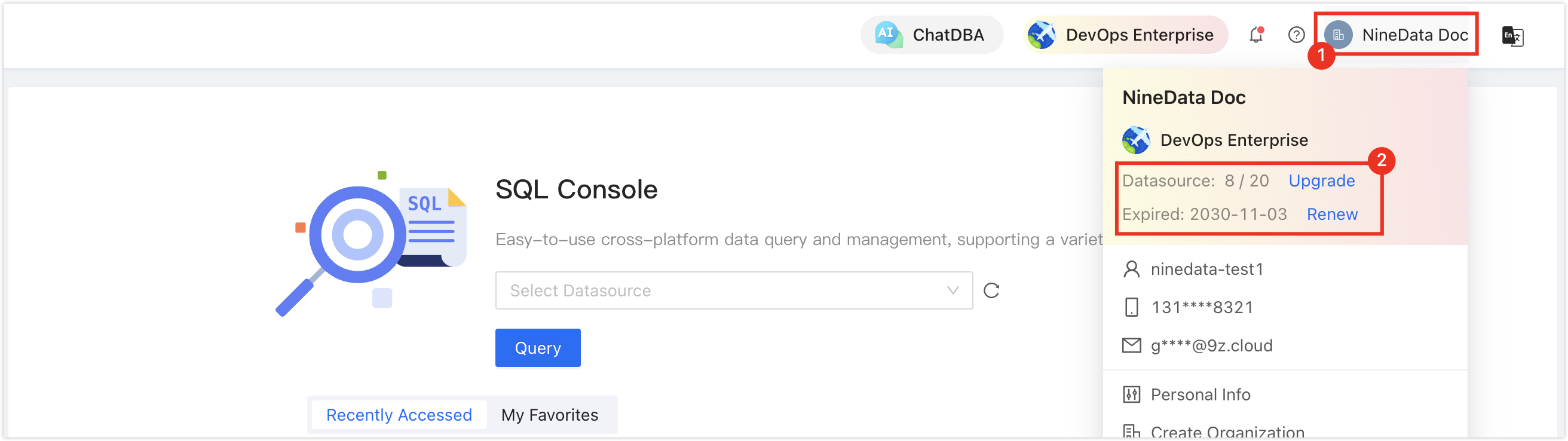
In the commercial versions (, ), please ensure that your monthly/yearly subscription is not expired, as it may result in the inability to use the Database DevOpsservice. You can quickly check the remaining quota and expiration date at the top right corner of the NineData console page.
Operation Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
Click on in the left navigation bar.
tipIf you have previously logged in to the data source and have not closed it, you will automatically enter the data source page.
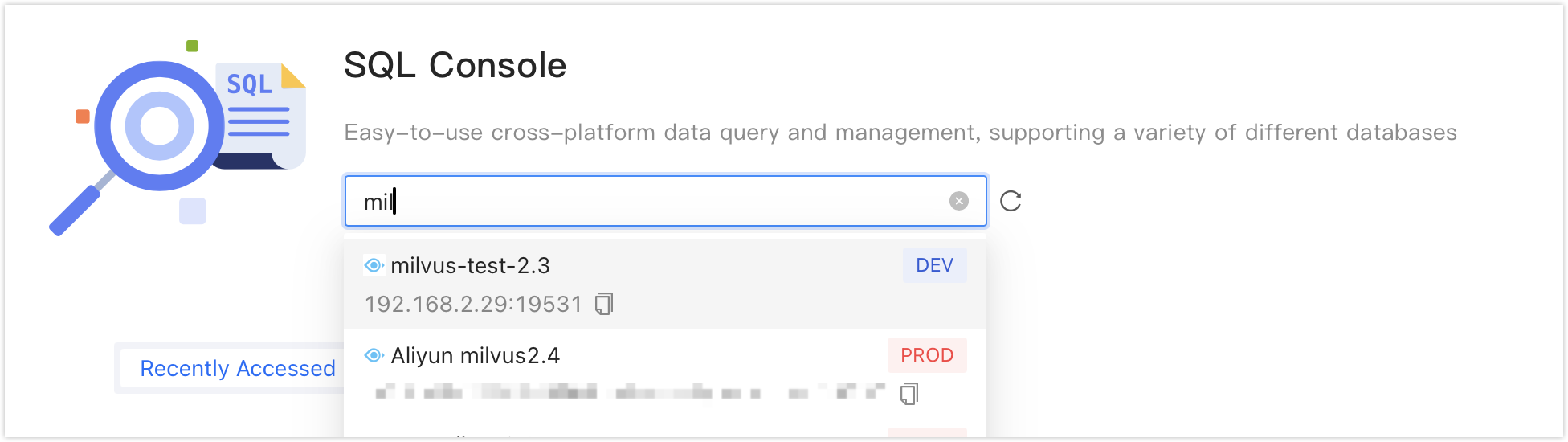
Click on the text box under , and a list of available data sources will pop up. Click on the target data source and click to jump to the SQL Console.
tip- If you haven't created Data Source before, a blank page will be displayed. In this case, please click on on the page.
If there are multiple data sources, you can enter all or part of the keywords in the box for exact or fuzzy search. The following fields are supported for search:
Data source name
IP address
After opening the SQL Console, you can perform data development operations on the data source. For detailed usage of the SQL Console, please refer to Interface Description.
Interface Description
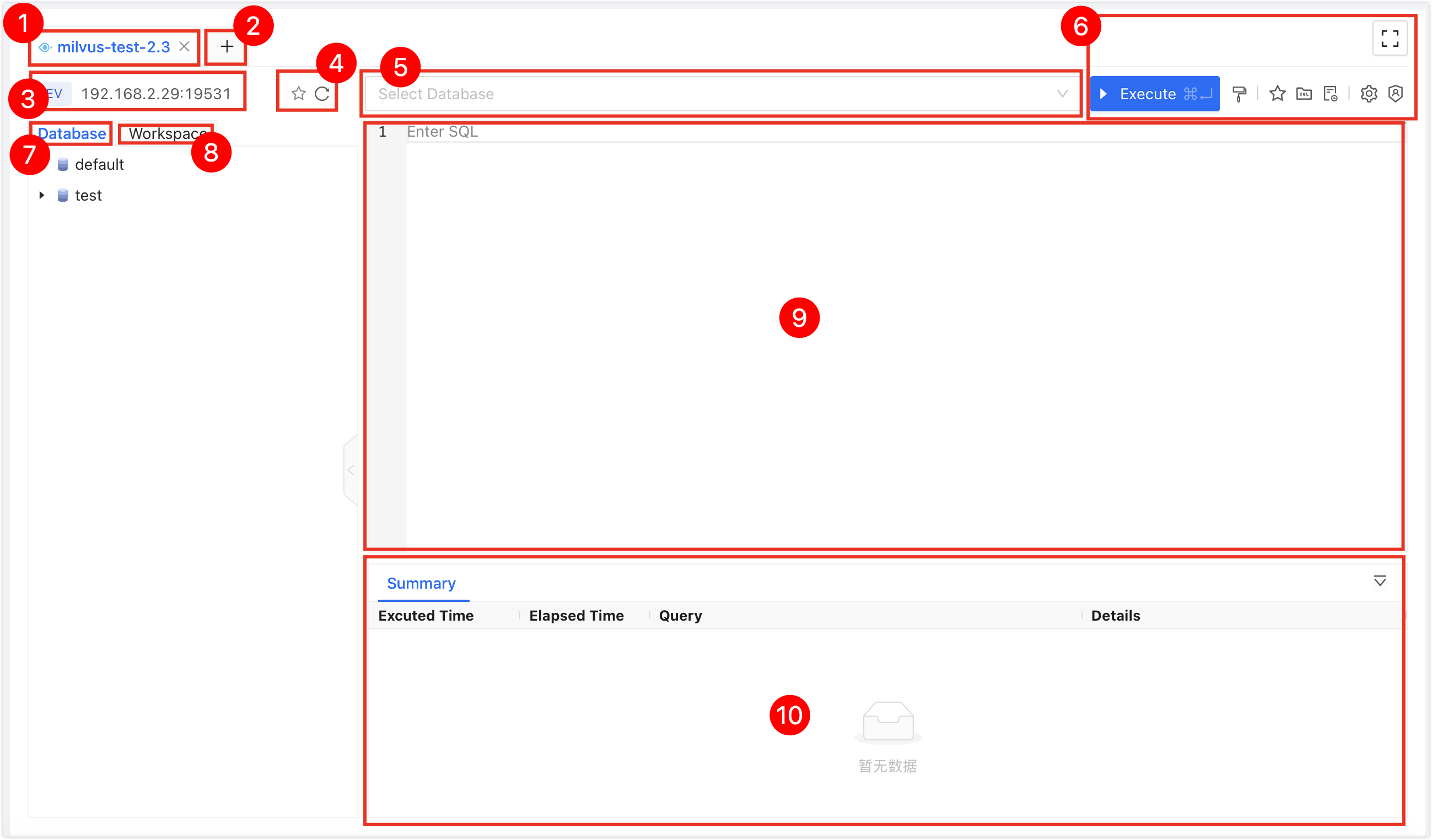
| No. | Function | Introduction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SQL Console Tab | Represents the currently opened data source SQL Console. Multiple SQL Consoles can be switched by clicking on the tabs, and the SQL Console can be closed by clicking the X on the right side of the tab; double-clicking the tab can change the tab name; dragging the tab can adjust the position of the tab. The right-click menu supports the following operations:
|
| 2 | Open Data Source | Select and open a new data source SQL Console. |
| 3 | Data Source Information | Display information about the current SQL Console's data source, including environment, IP address, and port number. Right-click menu:
|
| 4 | Favorite|Refresh |
|
| 5 | Database Name | Select the target database to perform SQL operations. |
| 6 | Function Buttons |
|
| 7 | Database Object Tree | Displays all databases, tables, columns, and other objects in the current Milvus in a tree format. You can perform the following operations:
|
| 8 | Workspace | Placeholder. |
| 9 | Editor Window | Supports the following features:
|
| 10 | Execution Information, Result Set | Displays the execution information and result set of the command.
|
Appendix I: SQL Syntax Design
DDL
| Category | Command | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| Database Operations | Create Database | CREATE DATABASE <Database Name> |
| Delete Database | DROP DATABASE <Database Name> | |
| Table Operations | Create Table | CREATE TABLE <Table Name>( <Primary Key Name><Data Type> PRIMARY KEY, <Column Name><Data Type>(<Length>) [PROPS Attribute][NOT NULL|NULL][comment 'Comment'], INDEX <Index Name>(<Column Name>) [PROPS Attribute] ) |
| Modify Table Properties | ALTER TABLE <Table Name> SET PROPS(<Table Properties>) | |
| Rename Table | RENAME TABLE <Table Name> TO <New Table Name> | |
| Delete Table | DROP TABLE <Table Name> | |
| Load Table | LOAD TABLE <Table Name> | |
| Release Table | RELEASE TABLE <Table Name> | |
| Index Operations | Create Index | CREATE INDEX <Index Name> ON <Table Name>(<Column Name>) PROPS(<Properties>) |
| Delete Index | DROP INDEX <Index Name> ON <Table Name> | |
| Alias Operations | Create Alias | CREATE ALIAS <Alias> FOR <Table Name> |
| Delete Alias | DROP ALIAS <Alias> |
Example:
--Create a simple table
create table t1(
id bigint primary key, -- Primary key column
vector vector(3), -- 3-dimensional floating-point vector
name varchar(32), -- Short text field
age int, -- Numeric field
index idx1(vector) props( -- HNSW vector index
index_type=HNSW, -- Index type
M=16, -- Inter-layer connections
metric_type=COSINE, -- Similarity calculation method
efConstruction=128), -- Construction parameter
index idx2(age)
);
--Create a complex table
create table t2 (
id bigint primary key,
c2 int64 props(is_partition_key=true) not null, -- Partition key
c3 float null comment 'abc',
c4 double comment 'c4 column comment',
c5 vector(32), -- Standard floating-point vector
c6 int[45], -- Fixed-length array
c7 json, -- JSON document
c8 varchar(2541) default 'abc',
c9 varchar(10)[21],
c10 float[32],
c11 binary_vector(128), -- Binary vector
c12 sparse_float_vector(128), -- Sparse vector
c14 int8,
c15 int16,
c16 int32,
c17 varchar(256) comment 'String test',
c18 vector(32),
index idx1(c3),
index idx2(c2) props(type=autoindex),
index idx3(c5) props(type=ivf_flat,nlist=10,metric_type=COSINE), -- IVF_FLAT vector index
index idx4(c11) props(type=BIN_IVF_FLAT,nlist=10,metric_type=HAMMING), -- Binary vector index
index idx5(c12) props(type=SPARSE_INVERTED_Index,metric_type=IP),
index idx6(c18) props(type=HNSW,M=31,metric_type=L2,efConstruction=124),
index idx7(c8) props(type=inverted),
index idx8(c14) props(type=bitmap),
index idx9(c15) props(type=STL_SORT),
index idx10(c17) props(type=Trie)
) comment='test table' props(
enable_dynamic_field=true, -- Allow dynamic fields
collection.ttl.seconds=3600, -- Data automatic expiration time
ABC=234);
DML
| Category | Command | Syntax Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Insertion | Insert a Single Record | INSERT INTO <Table Name> (<Column Name 1>,<Column Name 2>) VALUES (<Value 1>,<Value 2>) |
| Insert Multiple Records | INSERT INTO <Table Name> (<Column Name 1>,<Column Name 2>) VALUES (<Value 1>,<Value 2>),(<Value 3>,<Value 4>) | |
| Insert via SET | INSERT INTO <Table Name> SET <Column Name 1>=<Value 1>, <Column Name 2>=<Value 2> | |
| Data Replacement | Replace Data | REPLACE INTO <Table Name> (<Column Name 1>,<Column Name 2>) VALUES (<Value 1>,<Value 2>) |
| Data Deletion | Delete by Condition | DELETE FROM <Table Name> WHERE <Condition Statement> |
DQL
| Category | Command/Function | Syntax Example |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Query | View Databases | SHOW DATABASES |
| View Tables | SHOW TABLES | |
| Full Table Query | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> | |
| Conditional Filtering | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> WHERE <Column Name 1> IN (1,2,3) | |
| Paging Query | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> LIMIT 10 OFFSET 20 | |
| Vector Retrieval | Single Vector Search | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> ORDER BY vector_search(<Vector Column Name>, [1.0,2.0,3.0]) |
| Vector Search with Parameters | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> ORDER BY vector_search((<Vector Column Name>, [1.0,2.0], nlist=10, metric_type=COSINE) | |
| Combined Filtering Conditions | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> WHERE filter='id>0' ORDER BY vector_search(<Vector Column Name>, [1.0,2.0,3.0]) | |
| Aggregation and Grouping | Group Retrieval | SELECT * FROM <Table Name> GROUP BY <Column Name> PROPS(group_size=3) |
Example:
-- Normal Query
select * from table_name
select id,c1 from table_name where id=1
select * from table_name where id in (1,2)
select * from table_name where id in (1,2,3) limit 10
select * from table_name where id in (1,2,3) limit 10,20
select * from table_name where filter='id==3' limit 10
select * from table_name where filter='id in [1,2,8]' limit 10 offset 20
select * from table_name where filter='age>15 and age<81' limit 10,20
select * from table_name where filter='TEXT_MATCH(text, \'test deep\') and id>0';
select * from t123 where id in (14641243,88282101)
and filter='id>0 and name like "beyond%"'
limit 2;
-- Vector Query
select * from table_name
order by vector_search(column_name,{vector_value})
limit 10
select id,text from table_name
order by vector_search(column_name,{vector_value},nlist=10,param2=2)
limit 10
select id,text from table_name
where filter='id>0'
order by vector_search(column_name,{vector_value},nlist=10,radius=0.4,range_filter=0.6)
limit 10
select * from t123 where filter='id>0'
group by docId
order by vector_search(vector,[1,2,1])
props(group_size=3,strict_group_size=false)
select version()
select embedding('男士','text-embedding-v3',64)
Permission Control
| Category | Command | Syntax Example |
|---|---|---|
| Role Management | View Roles | SHOW ROLES |
| Create Role | CREATE ROLE <Role Name> | |
| Grant Role | GRANT <Permission> ON <Scope> TO <Role Name> | |
| Revoke Permission | REVOKE <Permission> ON <Scope> FROM <Role Name> | |
| User Management | View Users | SHOW USERS |
| Create User | CREATE USER <User Name> IDENTIFIED BY '<Password>' | |
| Bind Role | GRANT <Permission>, <Role Name> TO <User Name> |
Example:
-- Role management example
create role role1; -- Create role role1
grant CreateDatabase,DropDatabase on Global to role1; -- Grant the permission to create and delete databases globally to role1
grant Delete,Insert on Colleciton to role1; -- Grant the permission to delete and insert within the collection to role1
revoke Delete on Colleciton from role1; -- Revoke the delete permission from role1 within the collection
-- User management example
create user user1 identified by 'abc123'; -- Create a user named user1 with password abc123
grant admin,role1 to user1; -- Bind the administrator role and role1 to user1
desc user user1; -- Display all roles owned by user1
desc role role1; -- Display all permissions owned by role1
Appendix II: Function Syntax Table
| Function Name | Function Purpose | Parameter Definition | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|---|
VECTOR_SEARCH | Execute vector similarity calculation, used for sorting during retrieval |
| SELECT * FROM <Table Name> ORDER BY vector_search(vector_col, [0.1,0.2,0.3], nlist=10) |
EMBED | Convert text to vector |
| INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (1, 'text', embed('男士', 'text-embedding-v3', 64)) |
VERSION | Return database version information | No parameters | SELECT VERSION() |