NineData vs Yearning
NineData and Yearning are both products in the field of database DevOps. Yearning primarily focuses on providing SQL audit capabilities for MySQL databases, while NineData is a comprehensive database DevOps platform that supports a wider range of functionalities and database types.
NineData surpasses Yearning comprehensively in terms of product features. Additionally, NineData offers a permanently free version of its Database DevOps Professional Edition 10 with 10 data source specifications under the SaaS model. Users can register and start using it immediately without the need for application servers and database hardware preparation, making it very convenient for small and medium-sized teams.
Features Comparison
| Function Category | Function | Yearing | NineData |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Capabilities | Deployment Mode | Local Deployment | Cloud (SaaS), Local Deployment |
| Open Source | Open Source, AGPL License, Advanced Features Charged | Not Open Source, Free for Up to 10 Database Instances (Cloud Mode), Charges Apply Beyond 10 | |
| Data Source Support | 1 | 60 | |
| Cloud Platform Adaptation | ❌ | Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Baidu Cloud, China Mobile Cloud, AWS, GCP | |
| Login Mode | Username/password, SSO(LDAP) | Username/password, SSO(LDAP), WeChat | |
| Language Support | Chinese | Chinese, English | |
| Database DevOps | SQL Console | Support | Support |
| Object Visualization Management | ❌ | Support for Tables, Views, Stored Procedures, Functions, Triggers, Events | |
| Query Result Set Operations | Viewing | Viewing, Modifying, Searching, Filtering, Exporting | |
| Session Isolation | ❌ | Support | |
| SQL Audit and Deployment | SQL Change Deployment | Support | Support |
| Change Automatic Backup | Support | Support | |
| Approval Process | Support | Support | |
| OnlineDDL | Support | Support | |
| OnlineDML | ❌ | Support | |
| Built-in SQL Specifications | 40+ | 100+ | |
| Mobile Approval | Support (Sponsorship Required) | Support | |
| Release Process Orchestration | ❌ | Support | |
| Data Security | Sensitive Data Protection | Support but Not Rigorous, Easily Bypassed | Support |
| Permission Authorization Mode | Administrator Authorization | Administrator Authorization, User-initiated Application | |
| Permission Model | User, Role, Data Source | User, Role, Data Source, Environment Group | |
| Operation Audit | Support | Support | |
| Advanced Data Processing | Data Import | ❌ | Support |
| Data Export | ❌ | Support | |
| Data Archiving | ❌ | Support | |
| Data Tracking | ❌ | Support | |
| Database Union Query | ❌ | Support | |
| Performance Diagnosis | Slow SQL Performance Analysis | ❌ | Support |
| Session Management | ❌ | Support | |
| Others | AI Big Model Integration | ❌ | Support, Providing Text2SQL, AI SQL Diagnosis, ChatDBA |
Detailed Differences One: Product Installation and Deployment Modes
NineData: Default recommendation is the Cloud (SaaS) mode, where users can register an account on the official website and start using it immediately. It also provides a local deployment mode for enterprises with higher data compliance requirements (requires preparation of application and database servers).
Yearning: Open-source product on GitHub, exclusively adopts the local installation and deployment mode (requires preparation of application and database servers).
Detailed Differences Two: Open Source and Free
- NineData: Code is not open source. The Cloud platform offers a perpetual free version of the Database DevOps Professional Edition for up to 10 data sources, with charges applicable for more than 10.
- Yearning: Main functionalities are open source under the AGPL license, with some advanced features requiring sponsorship for access.
Detailed Differences Three: Supported Database Types
- NineData: Supports over 60 types of databases including MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, MongoDB, etc.
- Yearning: Only supports MySQL databases.
Detailed Differences Four: Cloud Platform Support
- NineData: Supports mainstream cloud platforms such as Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Baidu Cloud, China Mobile Cloud, AWS, etc. It enables automatic retrieval of cloud database information via Cloud platform APIs without manual input, and supports private network connection via VPC.
- Yearning: Does not integrate with cloud platforms.
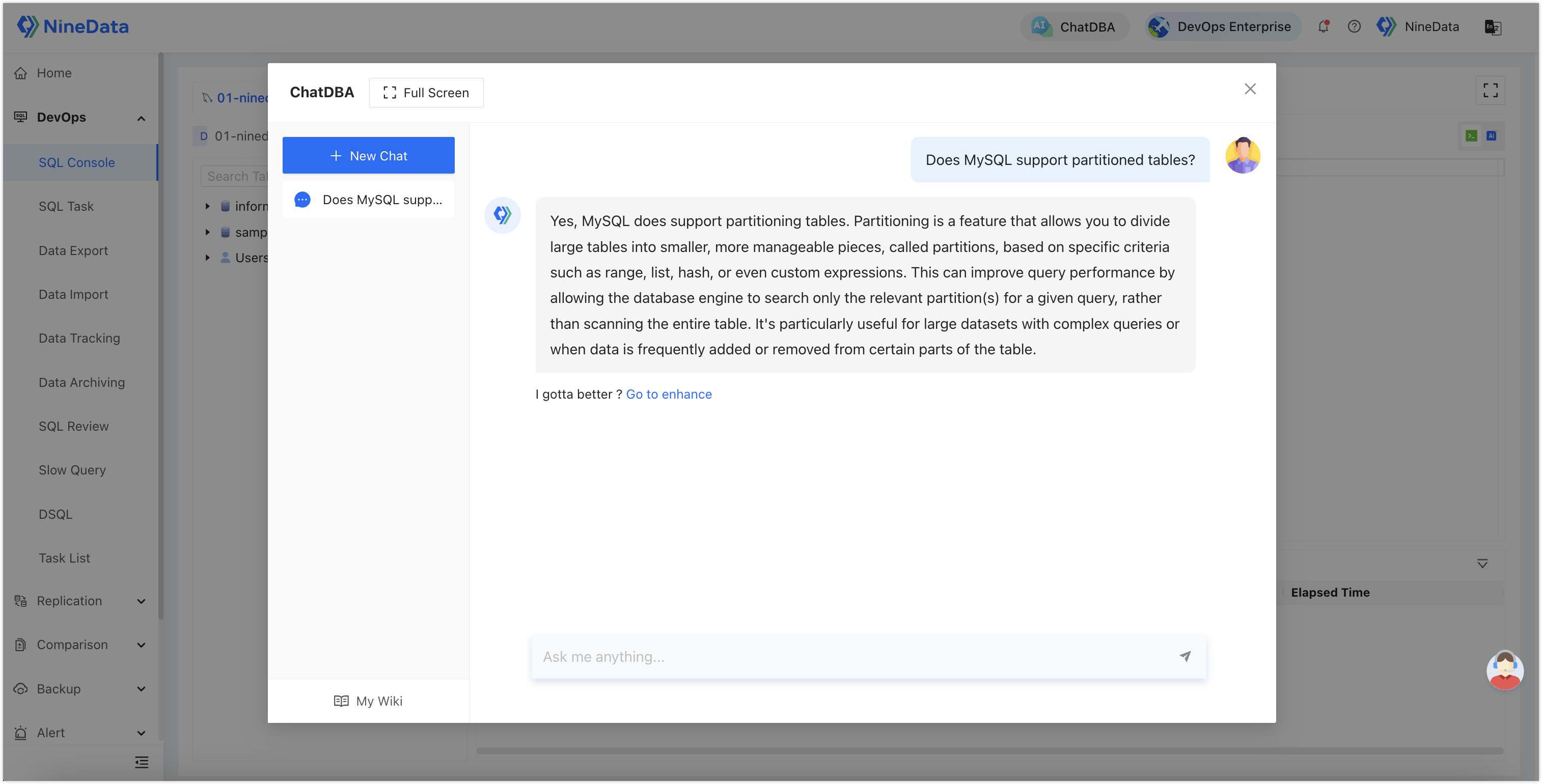
Detailed Differences Five: SQL Console
SQL editing window is the core functionality for developers to operate databases, similar to database client tools, and both products support it.
NineData: Provides a user experience similar to Navicat, DBeaver, supporting comprehensive object navigation, as well as visual operations on various objects like tables, views, stored procedures, etc. The SQL editing features include intelligent prompts for more precise and efficient editing. Result sets support editing, copying, searching, sorting, exporting, etc. Enterprises using NineData can eliminate the hassle of installing various database client tools.
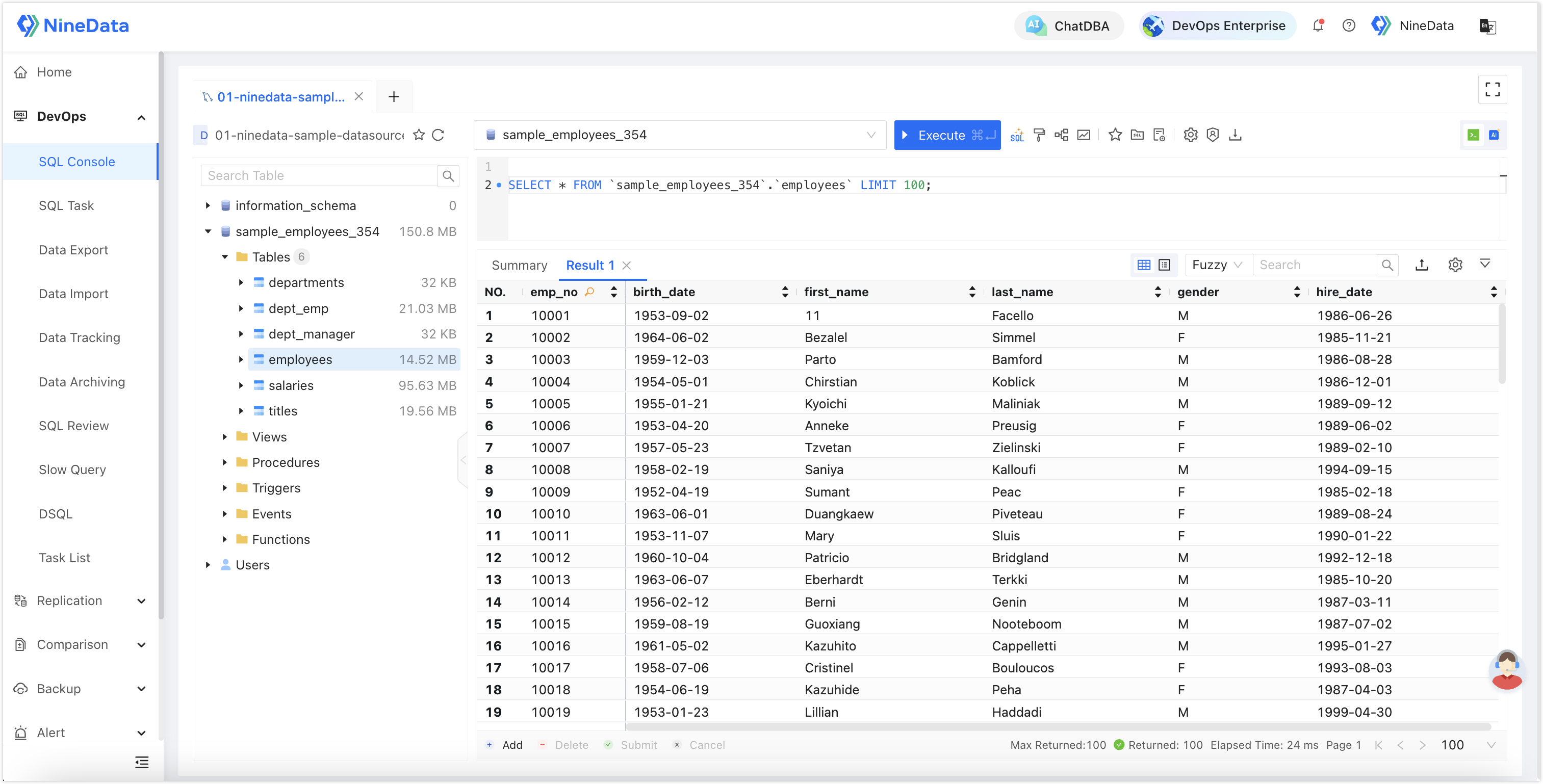
Yearning: Provides basic capabilities for SQL editing, code prompts, and displaying query results.
Detailed Differences Six: SQL Audit and Deployment
Main functionalities of Yearning include standard SQL task submission, audit, execution, and data change backup features. It supports OnlineDDL for MySQL databases.
Compared to Yearning, NineData has the following advantages in the above functionalities:
- OnlineDML: Valuable for correcting large batches of data, as it may affect business operations. NineData includes automated OnlineDML capabilities to improve operation efficiency and database stability by automatically executing changes in batches.
- SQL Rows Affected Analysis: Supports manual input of affected rows for changed SQL, and alerts users when there is a discrepancy between the automatically analyzed and user-inputted affected row numbers, avoiding SQL operation failures due to errors.
- SQL Task Pause: Supports manual pause of SQL tasks during execution.
Detailed Differences Seven: SQL Development Standards
SQL development standards are a crucial component of enterprise database development specifications, such as primary keys, field types, field naming conventions, etc., which are not provided by traditional client tools but are core capabilities of database DevOps products.
- NineData: Supports over 100 audit standards.
- Yearning: Supports over 40 audit standards.
Detailed Differences Eight: Sensitive Data Protection
Sensitive data protection is crucial for preventing data leaks, and both NineData and Yearning provide data desensitization capabilities.
NineData: Offers rigorous sensitive data protection and recognition capabilities, automatically desensitizing various complex SQL.
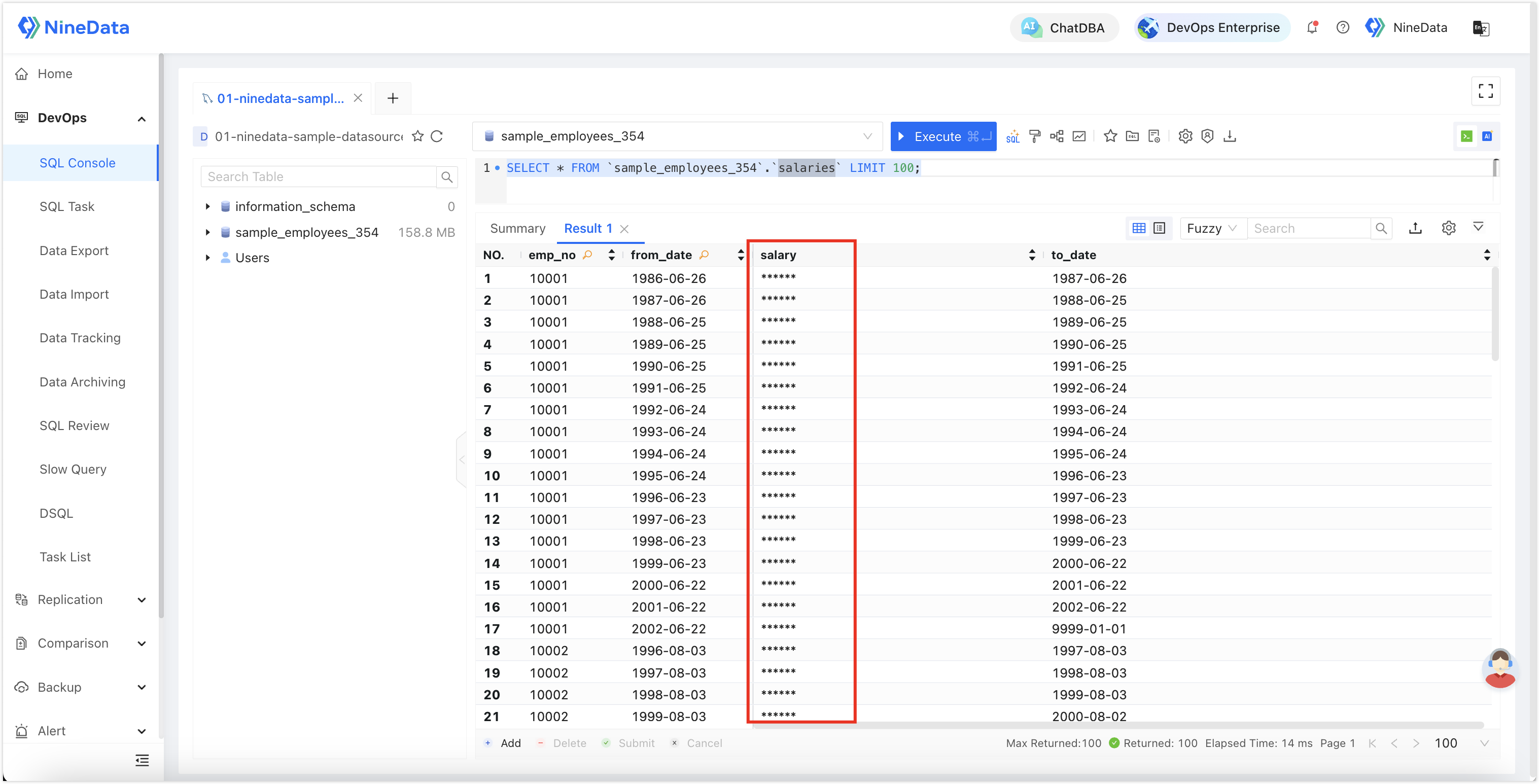
Yearning: Although it has sensitive data field configuration functionality, it can be easily bypassed with SQL, rendering it ineffective. It should not be used in production environments.
Detailed Differences Nine: Permission Handling Modes
NineData: Provides two permission management methods—administrator granting and user-initiated application. For enterprises with hundreds of users, user-initiated permission application is more efficient and supports hierarchical approval, relieving the pressure on administrators.
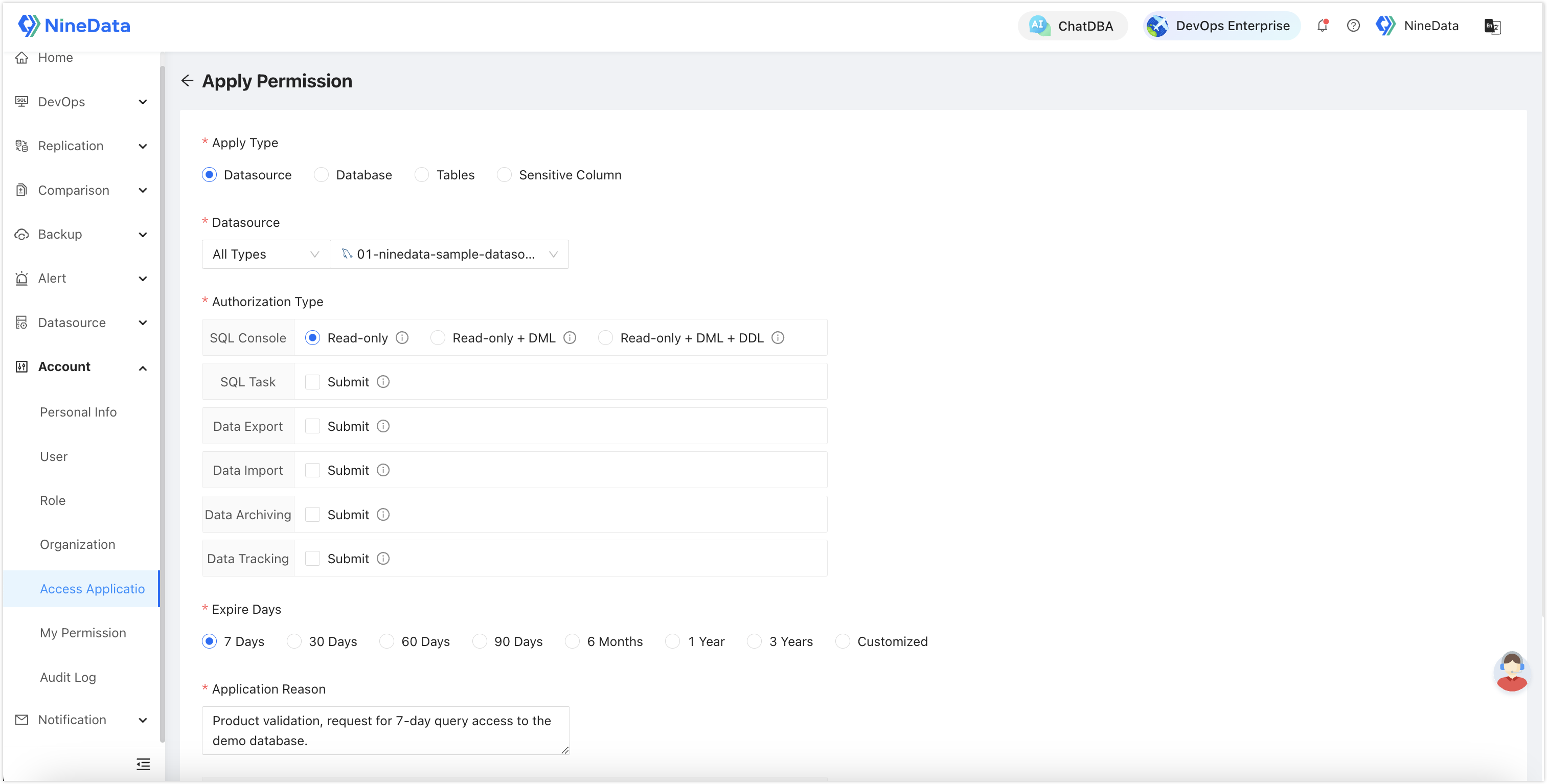
Yearning: All permissions for ordinary users need to be granted by administrators on the backend.
Detailed Differences Ten: Multi-language Support
- NineData: Chinese, English.
- Yearning: Chinese.
Advanced Features Supported by NineData but Not Yearning
Data Import: Suitable for importing large batches of data into databases, supporting single-file sizes up to 5 GB, and supporting SQL scripts or CSV file formats.
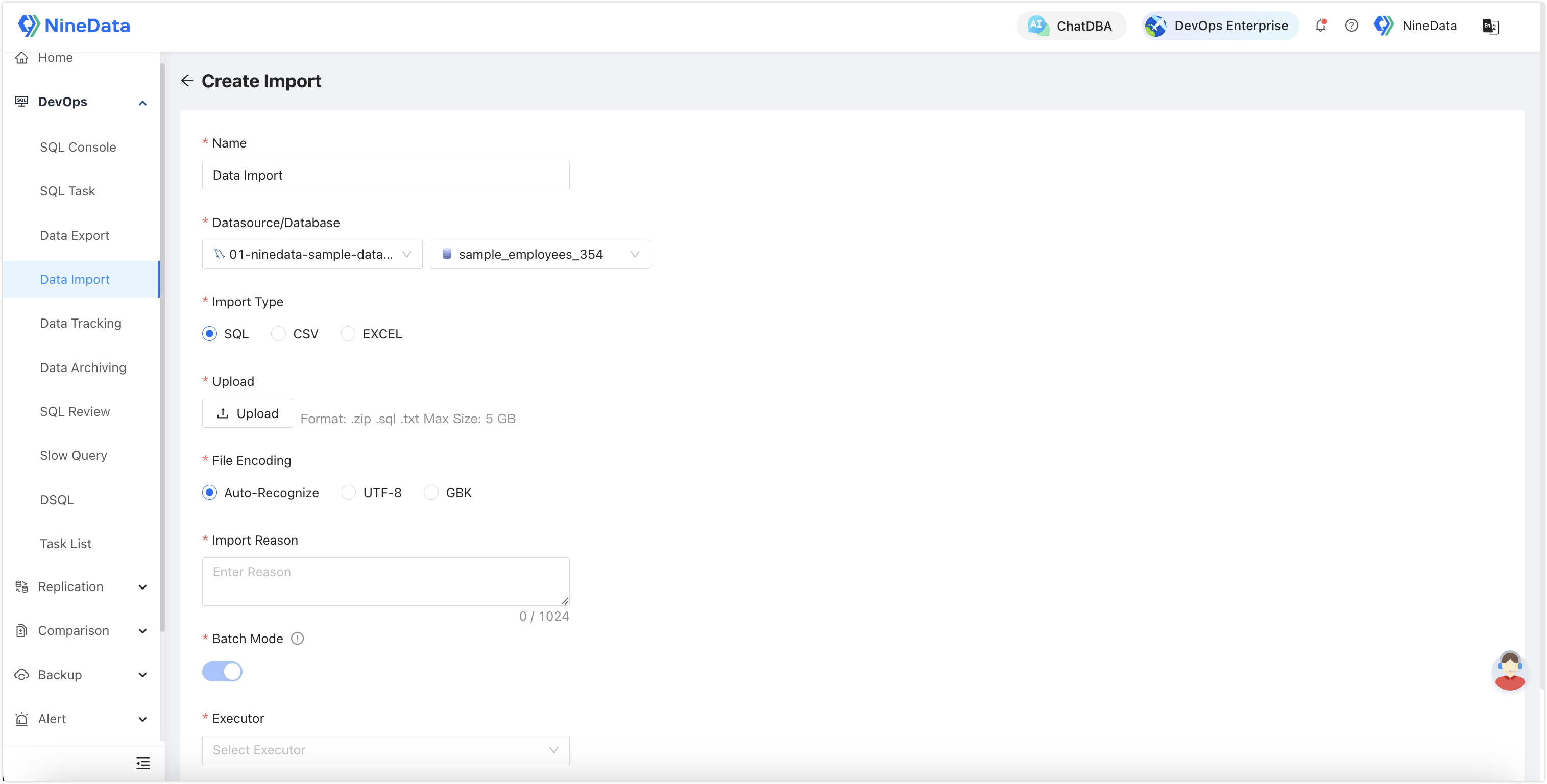
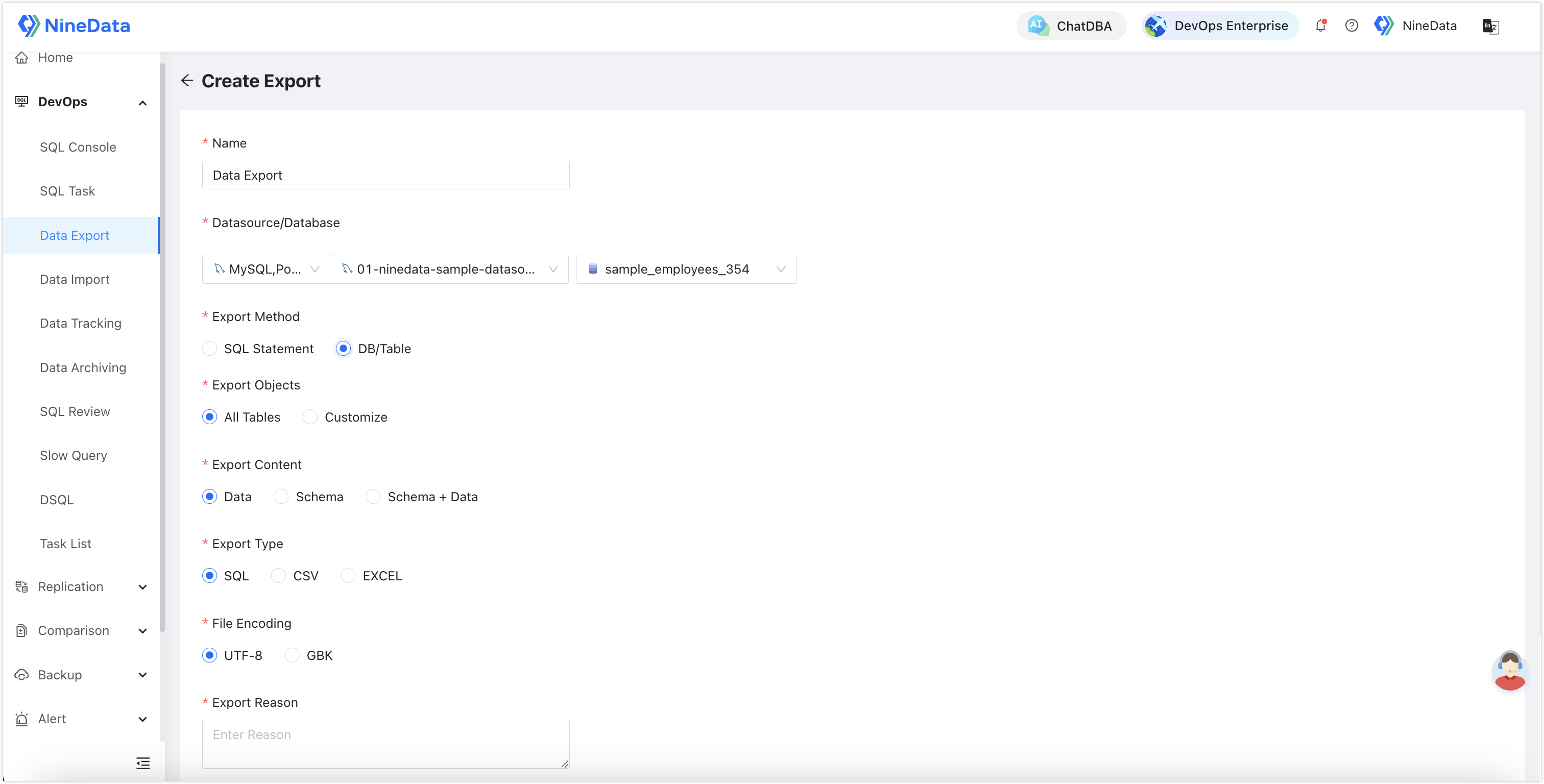
Data Export: Suitable for quickly exporting data, supports automatic data export desensitization, and allows selection of entire databases, multiple tables, or exporting via SQL statements.
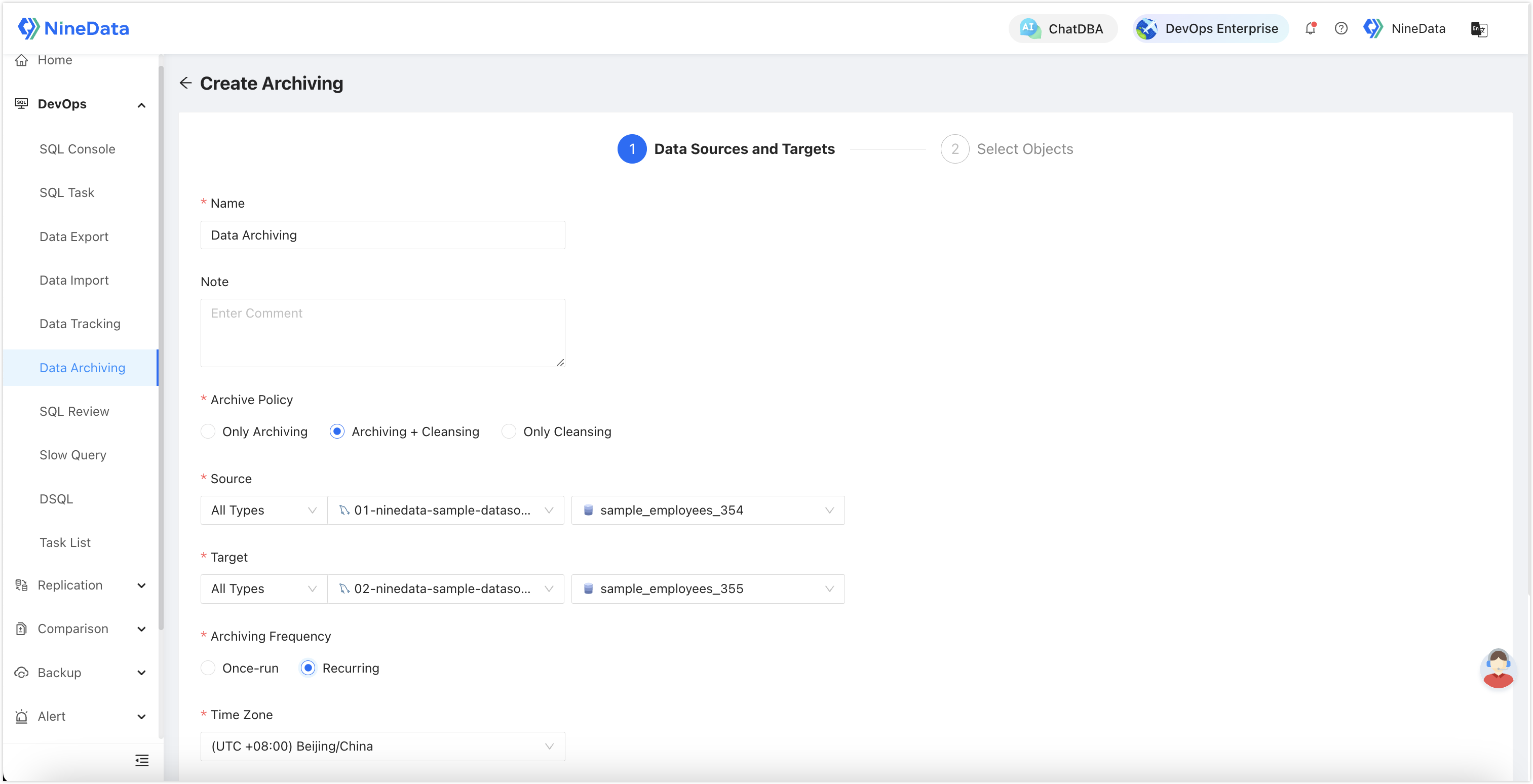
Data Archiving: Used for archiving historical data, allowing configuration of cleanup rules and scheduled execution.
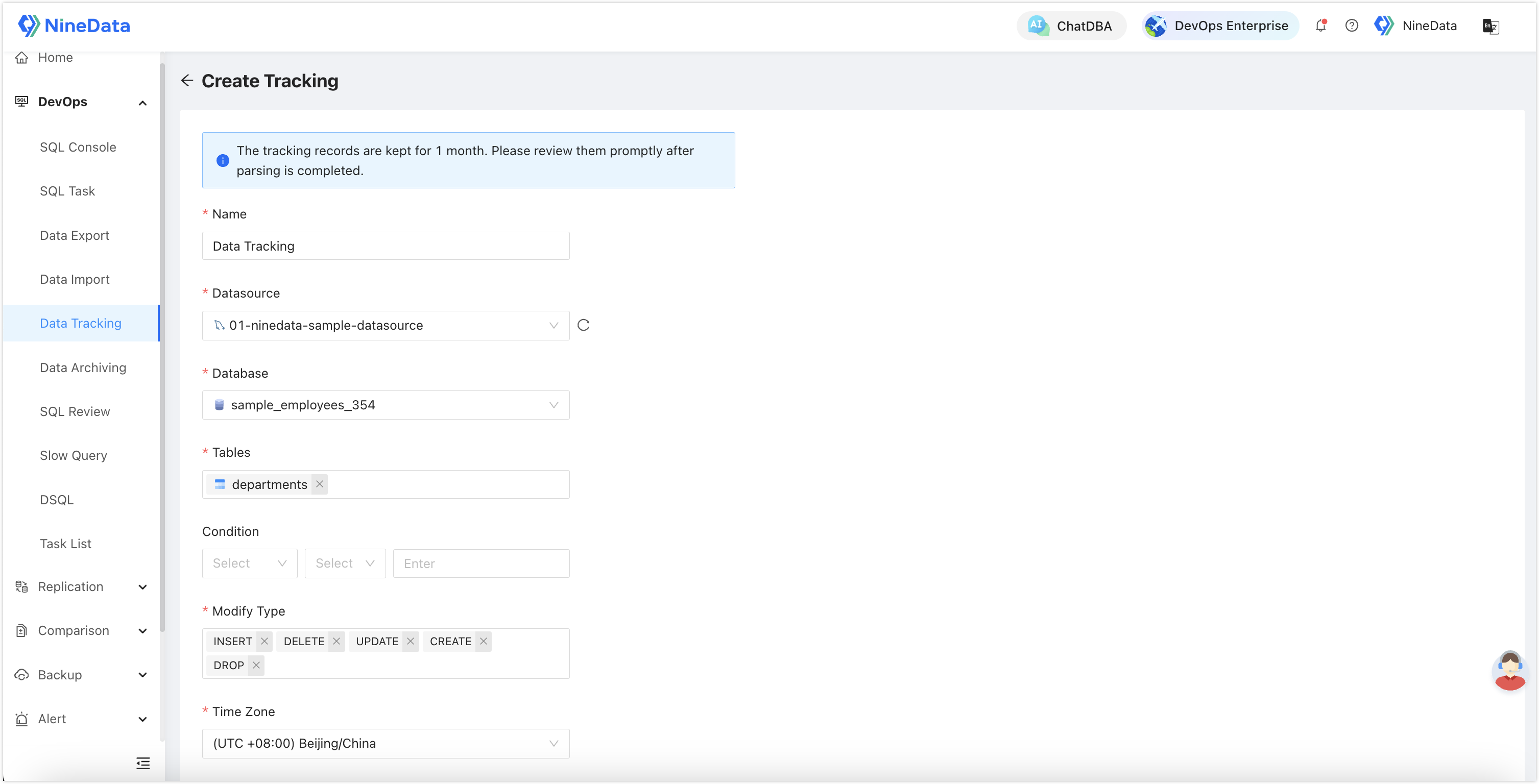
Data Tracking: Supports querying historical data change tracking, suitable for quick rollback after accidental operations, currently supporting MySQL databases.
Session Management: Supports real-time session status queries for databases, killing sessions, and statistical grouping by client, login user, and session status.
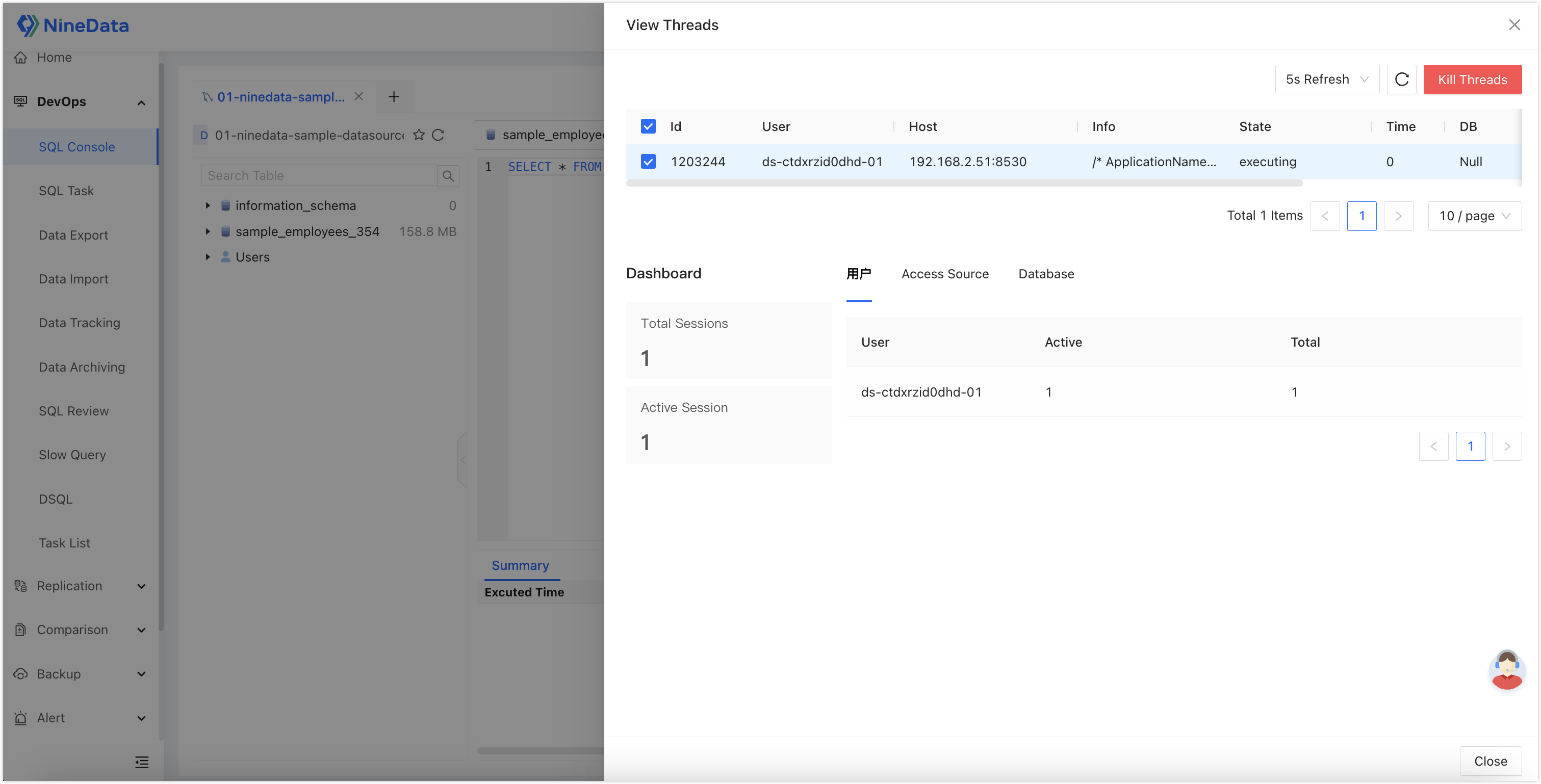
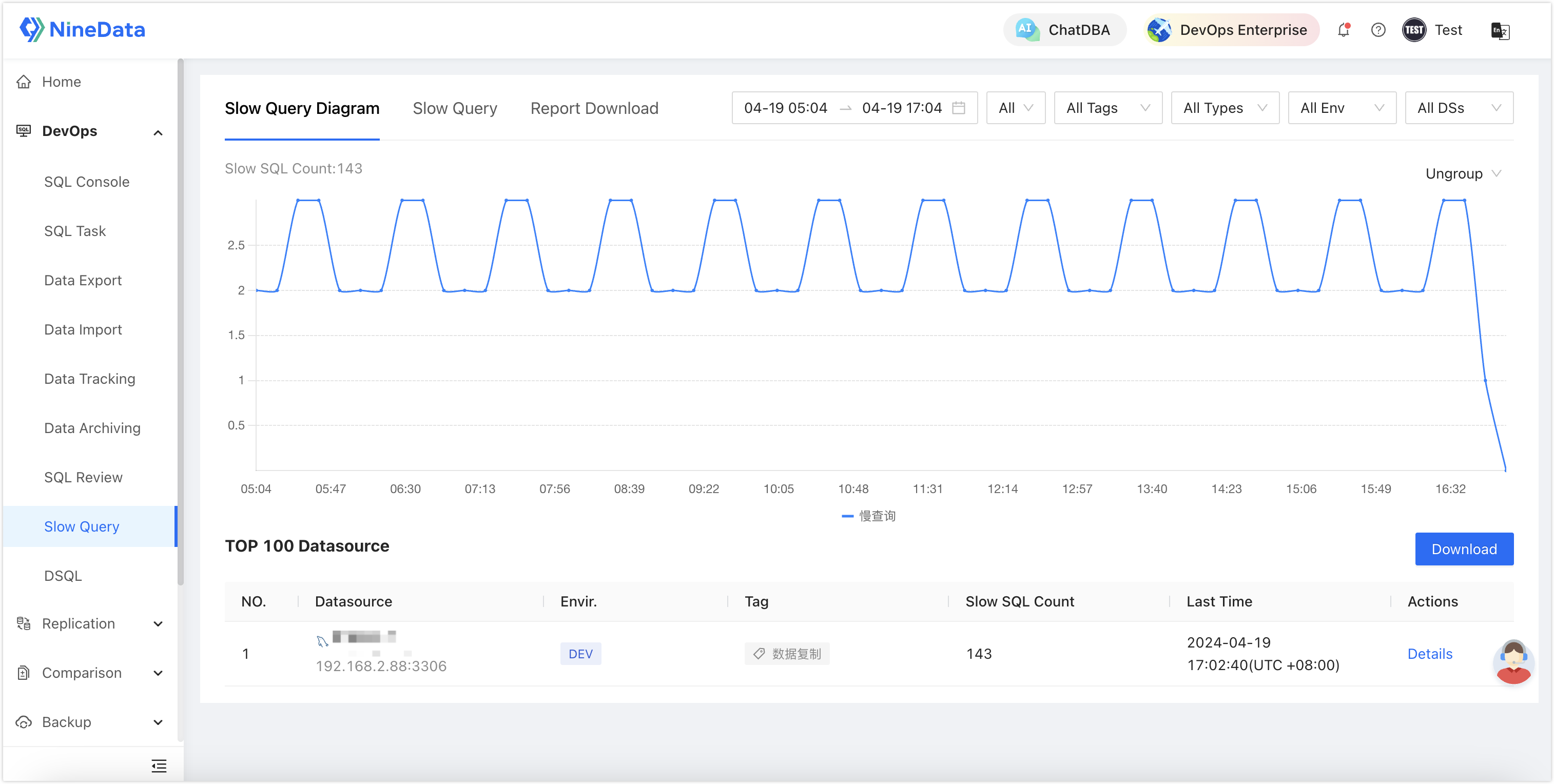
Slow SQL Management: Supports automatic collection, analysis, and diagnosis of historical SQL executions in databases.
Development Process Orchestration: Provides database CI/CD capabilities, supporting enterprise configuration of database release processes for development, testing, production environments, etc.

AI Big Model Integration: Based on large model AI technology, provides innovative capabilities such as natural language generation of SQL, SQL intelligent optimization, ChatDBA, etc.