SQL tasks
The SQL task is the task of initiating SQL operations on the database, mainly including SQL statements such as DDL (Database Definition Language) and DML (Database Manipulation Language). This article describes how to use SQL tasks.
Feature
To ensure data security, users who do not have write permissions to the target data source cannot make changes to its contents. If you have no permission or certain operations are governed by SQL development standards and have a change request, you can submit an SQL task ticket to achieve it. NineData's SQL task function provides full-cycle security control, including submission, approval, execution, rollback, and other steps.
To prevent unforeseen circumstances or data errors caused by operational mistakes, the system automatically backs up the current data state before executing the corresponding SQL task. In case of an error, you can download the backup data and manually roll back the changes to ensure data safety.
Precautions
In the commercial versions (DevOps Pro, DevOps Enterprise), please ensure that your monthly/yearly subscription is not expired, as it may result in the inability to use the Database DevOps service. You can quickly check the remaining quota and expiration date at the top right corner of the NineData console page.
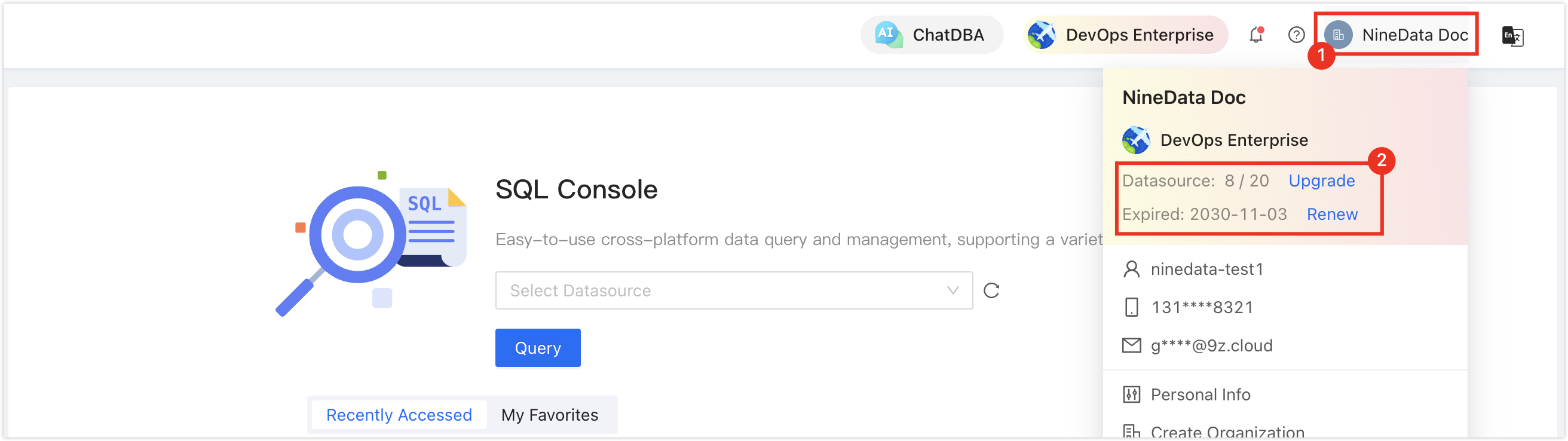
- The system automatically retains the backed-up data for 7 days, after which it expires automatically.
Prerequisites
The data source type must be one of the following: MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, OceanBase Oracle, OceanBase MySQL, Db2, PostgreSQL, Doris, SelectDB, Redis, MongoDB, DaMeng, KingBase, Klustron, DWS, openGauss, GaussDB, TiDB, GreatSQL, GBase, GaiaDB, GaiaDB-X, TDSQL MySQL, Lindorm, PolarDB-X.
To use the automatic backup feature, the data source type must be MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Greenplum, KingbaseES, PolarDB-X.
Submit SQL Change Task
Prerequisite
- An organization has been created or joined. For more information, see Managing Organizations.
- The NineData console is in organization mode. How to switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switching to Organization.
- The current user has access to the SQL Tasks module. For more information, see the Preset role permissions.
Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation bar, click DevOps> SQL Task.
tipIf no SQL Task are found, verify that the console is in organization mode. How to switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switching to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, click Create SQL Task in the upper right corner.
tipIf you haven't created SQL task before, a blank page will be displayed. In this case, please click on Create SQL Task on the page.On the Create SQL Task page, configure the ticket according to the table below.
Parameter Description Name Enter a name for the SQL task, which usually includes the purpose of the SQL statement. To reduce communication costs, use a meaningful name as much as possible. Supports up to 64 characters. Datasource The data source or the database group where the target database to be changed is located. Database|Schema The database or schema where the SQL change needs to be executed. Executor The person who will execute the SQL statement after the current SQL task is approved.
Note: The options in the Executor list depend on two situations:- If the current data source is configured with SQL Dev Policy, the options in the list are based on the SQL Task Executor Config rule configured in the current policy. This rule is located on the SQL Task & Console tab. For information on how to configure SQL Dev Policy, see Edit Policy.
- If the current data source is not configured with SQL Dev Policy, the options in the list are for users who have SQL Task - Exec permission for the current data source. For more information about authorization, see Configure User Permissions.
Estimated Affected Rows Enter the estimated number of rows that this change is expected to affect. During the Policy Pre-check stage of the SQL task, the system will verify whether there is a discrepancy between the actual number of rows affected by SQL and the estimated number. If they are not the same, a prompt will be given. Note (optional) Notes for the current SQL task that are not yet completed, such as the reason for executing the task, the expected execution time, etc. Submission Method Enter the SQL statement to be executed or upload a file containing the SQL statement. - SQL Text: Enter the SQL statement to be executed directly in the text box.
- SQL File: Click Upload File and select and upload a file containing the SQL statement.
Note: After the upload is complete, move the mouse to the file name, and you can select(preview file) or
(delete file) on the right side of the file name.
Rollback SQL (optional) For enterprises that require rollback plans for changes, the rollback SQL input provided here will be recorded within the current SQL task. However, it will not have any impact during the entire lifecycle of the current SQL task and is solely used for compliance purposes. Click on Save and Pre-Check to go to the Policy Pre-check page. The system will perform a pre-audit of the SQL statement based on the SQL development specification associated with the current data source, and there will be several results:
- Pre-audit passed: Depending on the configuration of the approval process, the task status will be changed to Pending or Approved. If it is the former, please proceed to the next step; if it is the latter, the process ends.
- Pre-audit failed: The task status will be changed to Pre-Check Failed. You can click on Check Again in the upper right corner of the page to pre-audit again, or you can withdraw the SQL task and edit and submit it again.
tipThe pre-audit issues include four categories: Must Modify, Suggested, Syntax, and Permissions:
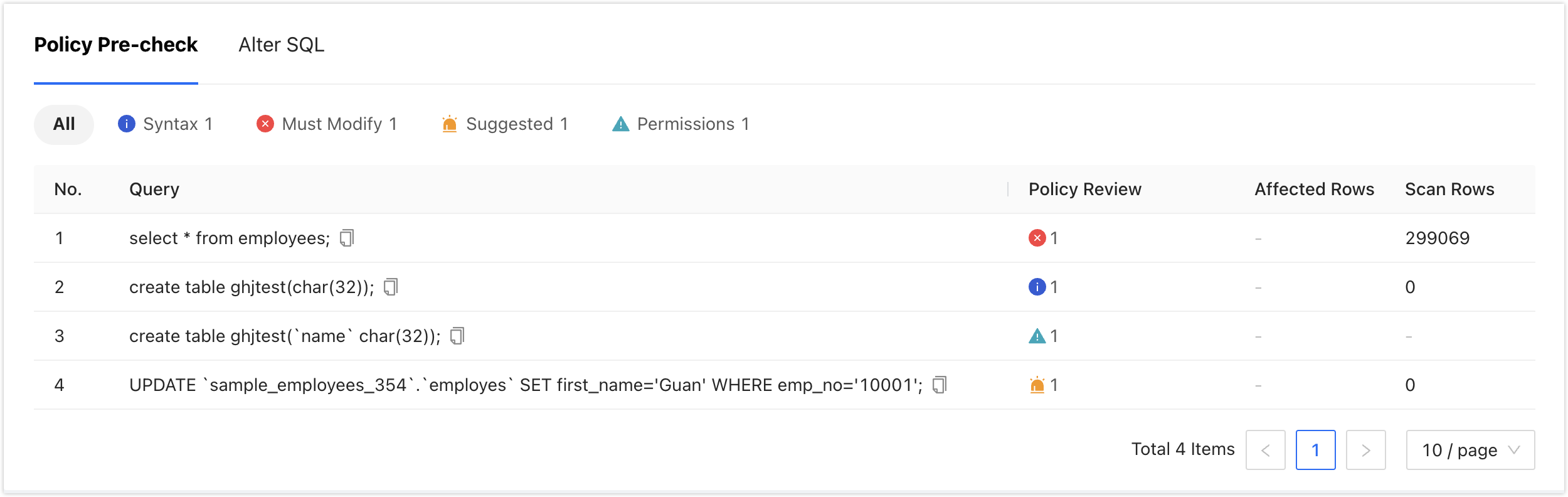
- Must Modify: Violation of the highest level specification configured by the administrator.
- Suggested: Violation of the suggested improvement specification configured by the administrator.
- Syntax: Attention is required for syntax issues automatically detected by the system. Although it does not block the SQL task process, the SQL may fail to execute. Please check the existence of databases and tables, as well as the correctness of the syntax.
- Permissions: Triggered two rules configured by the administrator in the SQL Development Guidelines, causing disruption in the SQL task workflow.
- Enable SQL task schema update type checking: Used to enable or disable SQL syntax related to structural changes.
- Allowed SQL Task Update Data: Used to enable or disable SQL syntax related to data modification.
Click on Submit Approval in the upper right corner of the page, select the process approver(s) in the pop-up window, and click on OK.
tip- Depending on the configuration of the approval process, the number of approvers to be selected here may be different. Please choose according to the actual situation.
If the Not Specifying Approvers feature is enabled in the current approval process, this section will display After submission, all approvers can review. Please check the results in the approval process.. You do not need to manually specify an approver; all personnel authorized to approve the current work order will receive approval notifications and be able to approve it.
The task status changes to Pending Approval. Before the approval is granted, you can perform the following operations:
- Withdraw: Withdraw the SQL task. For more information, see Withdraw the SQL task.
- Transfer: Change the approver of the SQL task.
Withdraw SQL Tasks
When the status of the SQL task is Pre-Checking, Pending Approval, Approved, or Scheduled, user can withdraw the application for the SQL task. After the withdrawal, the task will no longer be executed, and can re-edit the task list and submit it again.
Prerequisite
- The status of the SQL task is Pre-Checking, Pending Approval, Approved, or Scheduled.
- User is the Submitter of the SQL task or Administrator.
Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation bar, click DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf no SQL Task are found, verify that the console is in organization mode. How to switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switching to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, find the target SQL task, and click the task ID or Details in the Actions column to the right of the task. Click Withdraw in the upper right corner of the Details page.
tipUser can also click
> Withdraw in the Actions column to the right of the task.
In the confirmation window that pops up, click Withdraw or Withdraw and Edit.
- Withdraw: Task status changed to Withdraw. To re-edit the task, find the SQL task in the SQL Task list, and click Edit in the Actions column to the right of the task.
- Withdraw and Edit: The page automatically jumps to the edit page of the SQL task.
Approve SQL task
Prerequisites
- The status of the SQL task is Pending Approval.
- You are the Approver of the target SQL task or Administrator.
Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf you cannot find SQL Task, please make sure your console is in organization mode. For instructions on switching to organization mode from personal mode, see Switch to an organization.
On the SQL Task page, find the target SQL task and click its task ID or the Details in the Actions column to the right of the task.
On the Details page, review the contents of the Policy Pre-check and SQL Details tabs, and select Transfer, Approved, or Rejected as appropriate.
Operation Description Transfer Transfer the task to another user for approval. Approved Approve the request. After clicking Approved, you can enter Reason as needed and click OK. Rejected Reject the request and do not execute the SQL task. After clicking Rejected, you also need to enter Reason for rejection and click OK.
Execute SQL Tasks
You can execute a SQL task when its status is Approved.
Prerequisites
- The status of the SQL task is Approved.
- You are the Executor of the target SQL task or Administrator.
Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf you cannot find SQL Task, make sure that your console is in organization mode. For instructions on how to switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switch to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, click the task ID whose status is Approved.
On the Details page, click Execute in the upper-right corner.
In the pop-up Execute SQL Tasks window, select Errors Handling and Execution Method, and click OK.
Operation Description Errors Handling - If an error occurs, terminate the task.: Stop the execution immediately if an error occurs during SQL execution.
- Ignore errors, and Continue: Ignore the error during SQL execution and continue to execute.
- Rollback Task on Execution Error (MySQL only): Optional when the SQL task contains only DML statements. The task will be executed in a transactional manner, and if any DML statement fails, the entire task will be automatically rolled back to ensure atomicity and consistency.
Backup Failed Policy By default, SQL tasks are backed up for the changes before execution to prevent any adverse impact on business in case of execution errors. The following two options are supported: - Failed and Continue Task: Regardless of whether the backup is successful or not, the current SQL task will continue execution.
- Failed and STOP Task: After a backup failure, the current SQL task will not be executed.
Execution Method - Execute Now: Execute the SQL statement immediately.
- Scheduled Execution: Select a time to execute the SQL statement.
- Manual Execution: Manually execute the SQL in the SQL task, and click Executed, marked successful. You can also click Go to SQL Console to manually execute the SQL.
The task status has been changed to Running. If you do not need the system to backup your data before executing, you can click on the Skip Backup button in the upper right corner and then click Skip and Continue. Wait for the task status to change to Success.
Pause SQL Task
You can pause an SQL task when its status is Executing.
Prerequisites
- The SQL task status is Executing.
- You are an Administrator or the Executor of the target SQL task.
Procedure
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf SQL Task is not found, ensure that your console is in organization mode. To switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switch to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, locate the target SQL task and click on the task ID or the Details in the Actions column on the right side of the task. Click on Pause in the upper right corner of the Details page.
Terminate SQL Task
You can terminate an SQL task when its status is not in a terminal state (e.g., Success or Terminated). Once terminated, all ongoing operations will stop, and no further actions can be performed on the task.
Prerequisites
- The SQL task must not be in a terminal state.
- You must have the role of Administrator or be the Executor of the target SQL task.
Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation bar, click DevOps > SQL Task.
If SQL Task is not found, ensure that your console is in organizational mode. To switch from personal mode to organizational mode, refer to Switch to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, locate the target SQL task, then click on the task ID or the Actions column on the right side of the task and select Details. On the Details page, click Pause at the top right corner.
Restart SQL Task
You can restart an SQL task when its status is Executing or Failed.
Prerequisites
- The SQL task status is Executing or Failed.
- You are an Administrator or the Executor of the target SQL task.
Procedure
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf SQL Task is not found, ensure that your console is in organization mode. To switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switch to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, locate the target SQL task and click on the task ID or the Details in the Actions column on the right side of the task. Click on Restart in the upper right corner of the Details page.
In the pop-up Restart window, select Errors Handling, Backup Failed Policy, and Execution Method, then click OK.
Operation Description Errors Handling - If an error occurs, terminate the task.: If an error occurs during the execution of SQL, the execution will be terminated immediately.
- Ignore errors, and Continue: If an error occurs during the execution of SQL, the error will be ignored and the execution will continue.
Backup Failed Policy SQL tasks are backed up for changes before execution by default to prevent any impact on business in case of execution errors. The following options are supported: - Failed and Continue Task: Continue executing the current SQL task regardless of the success of backup.
- Failed and STOP Task: Do not execute the current SQL task if the backup fails.
Execution Method - Execute Now: Execute the SQL statement immediately.
- Scheduled Execution: Schedule the execution of the SQL statement at a specific time.
Downloading Backup Data
When an SQL task encounters an error and you need to restore the data to its pre-execution state, you can download the backup data of the target SQL task and manually roll back the data.
Prerequisites
- The object data source types for SQL tasks are MySQL and Oracle.
- The data backup status for the target SQL task is Finished.
- You are either Administrator or the Executor of the target SQL task.
- The backup file is not older than 7 days.
Procedure
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click on DevOps>SQL Task.
tipIf you cannot find SQL Task, please ensure that your console is in organization mode. To switch from personal mode to organization mode, see Switching to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, click on the target SQL task ID.
Click on More in the upper part of the page, and then click on Download on the right side of Data Backup.
The downloaded backup file is a
.zipcompressed file that contains the SQL files for rollback. You can upload this file by submitting another SQL task for data rollback. For more information, see Submit SQL Task.
View SQL Task List
Log in to the NineData Console.
In the left navigation pane, click on DevOps > SQL Task.
tipIf you cannot find SQL Task, please make sure that your console is in organization mode. For instructions on how to switch to organization mode from personal mode, see Switching to Organization.
On the SQL Task page, you can view all SQL tasks. If there are too many tasks, you can use the following search methods to filter the tasks and quickly locate the target task.
- Based on the workflow node of the task
- Based on the status of the task
- Based on the data source
- Based on the date
- Based on the task name or ID
- Based on the database name
NineData OnlineDDL
NineData's SQL tasks support the NineData OnlineDDL feature, which allows for database schema changes to be made without affecting normal database usage. For more information, see Perform non-locking structure changes to the table using NineData OnlineDDL.
Scope of Syntax for SQL Task Automatic Backup
To ensure accurate backup of data that is about to be modified before executing SQL tasks, NineData identifies SQL statements that may cause data or structural changes based on different database types. When an SQL task is submitted and enters the execution process, the system automatically backs up the affected tables, views, or objects to ensure safe rollback in case of misoperations or exceptions.
The scope of backup syntax for different databases is as follows.
PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL-like, Oracle
| Category | Syntax Triggering Automatic Backup |
|---|---|
| DML | UPDATE, DELETE |
| Table | ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME |
| View | ALTER VIEW, DROP VIEW |
| Function | ALTER FUNCTION, DROP FUNCTION |
| Procedure | ALTER PROCEDURE, DROP PROCEDURE |
| Trigger | ALTER TRIGGER, DROP TRIGGER |
MySQL
| Category | Syntax Triggering Automatic Backup |
|---|---|
| DML | UPDATE, DELETE |
| Table | ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME |
| View | ALTER VIEW, DROP VIEW |
| Function | ALTER FUNCTION, DROP FUNCTION |
| Procedure | ALTER PROCEDURE, DROP PROCEDURE |
| Trigger | ALTER TRIGGER, DROP TRIGGER |
| Event | ALTER EVENT, DROP EVENT |
SQL Server
| Category | Syntax Triggering Automatic Backup |
|---|---|
| DML | UPDATE, DELETE |
| Table | ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME |
| View | ALTER VIEW, DROP VIEW |
| Function | ALTER FUNCTION, DROP FUNCTION |
| Procedure | ALTER PROCEDURE, DROP PROCEDURE |
| Trigger | ALTER TRIGGER, DROP TRIGGER |