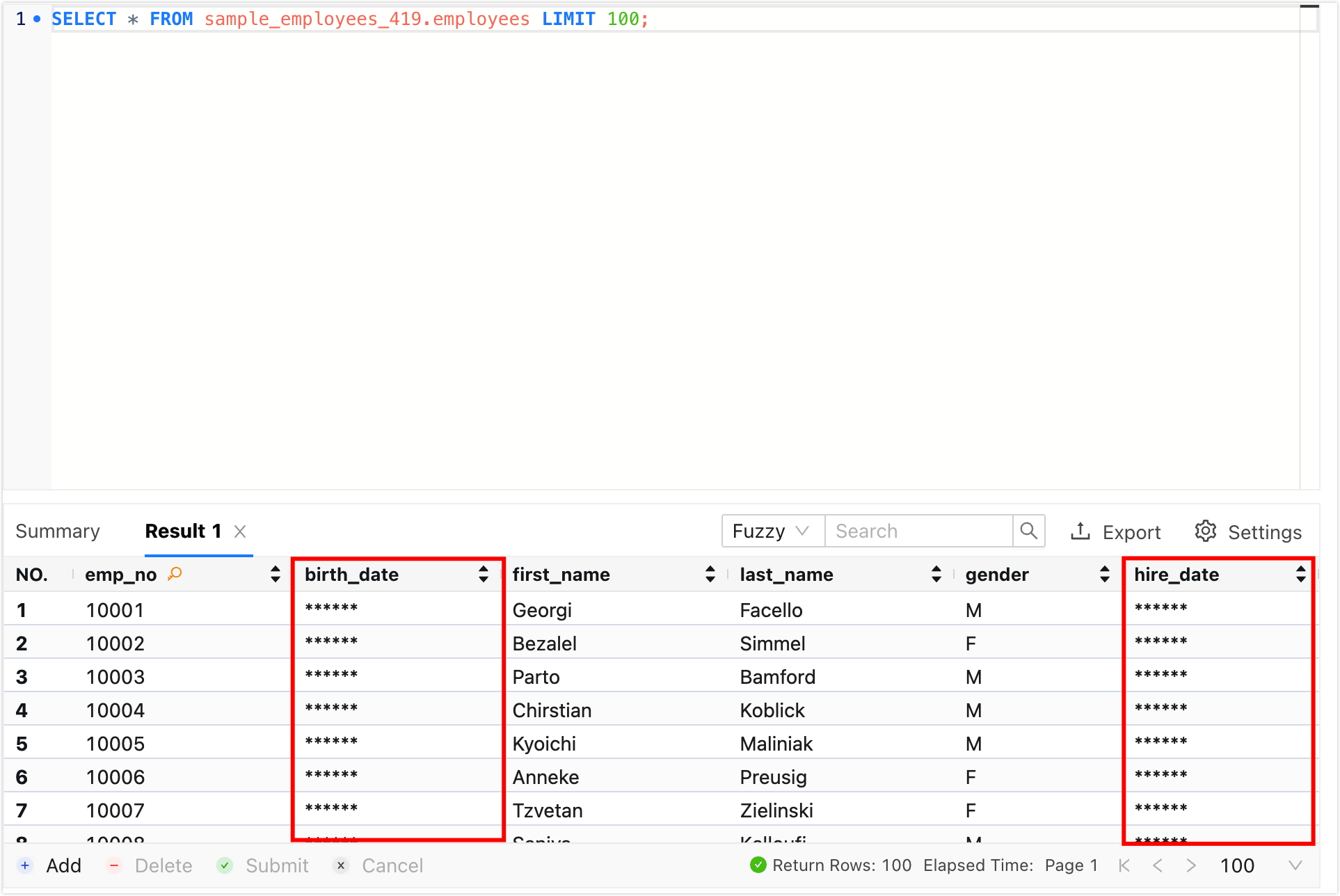
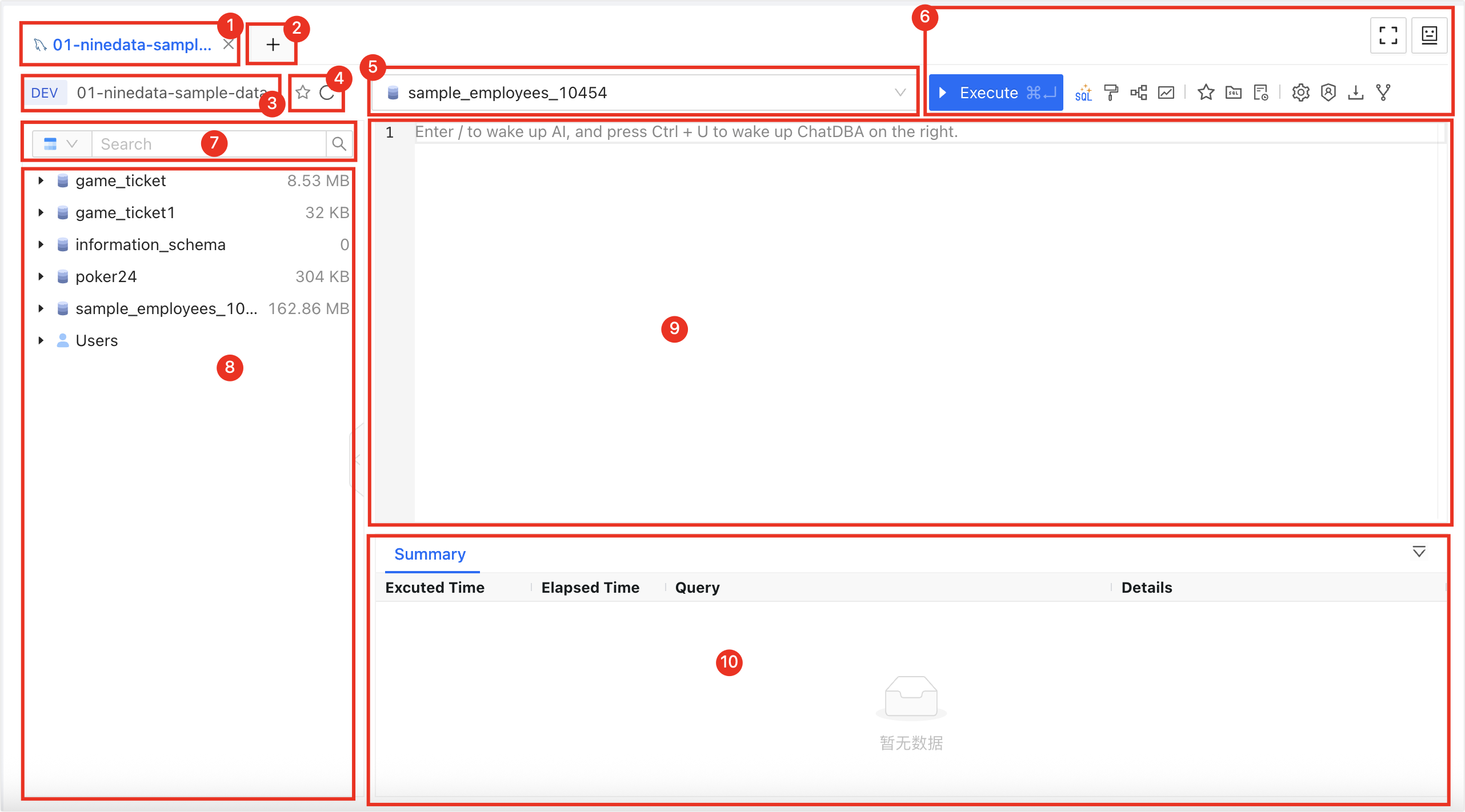
| 1 | SQL console tab | Indicates the currently open SQL Console for the data source. Multiple SQL Consoles can be switched by clicking on their tabs. Click the X on the right side of a tab to close the corresponding SQL Console. Double-click a tab to rename it, and drag a tab to adjust its position. The context menu supports the following operations:- Instance Details: Open the current data source details window.
- Rename Tab: Rename the current tab.
- Duplicate Query: Open a SQL Console for the current data source.
- New Query: Open a new data source SQL Console.
- Close Tab: Close the current tab.
- Close Others: Close all other SQL Consoles except the current one.
- Close Tabs to the Left: Close all SQL Consoles to the left of the current SQL Console.
- Close Tabs to the Right: Close all SQL Consoles to the right of the current SQL Console.
- Close All: Close all SQL Consoles.
|
| 2 | Open data source | Select and open the new data source SQL console. |
| 3 | Data source information | Display the data source information of the current SQL console, including the environment, IP address and port number. |
| 4 | Favorite|Refresh | - Favorite: Clicking the favorite icon adds the current data source to My Favorites, allowing for quick selection in a new SQL Console after addition.
- Refresh: Refresh the data in the current data source.
|
| 5 | Database name | Check the target database to perform the SQL operation. The effect is equivalent to the USEstatement. |
| 6 | Function |  : Execute Execute the selected SQL statement. : Execute Execute the selected SQL statement. : SQL Optimize AI intelligently analyzes the SQL statement on the cursor line and provides optimization suggestions. : SQL Optimize AI intelligently analyzes the SQL statement on the cursor line and provides optimization suggestions. : Format: Adjust the structure of the selected SQL statement to enhance readability. : Format: Adjust the structure of the selected SQL statement to enhance readability. : Execution Plan: View the execution plan of the selected SQL statement. : Execution Plan: View the execution plan of the selected SQL statement. : Favorite this SQL: Save all SQL statements in the current SQL Console to the SQL list for easy access next time. : Favorite this SQL: Save all SQL statements in the current SQL Console to the SQL list for easy access next time. : Favorites: View saved SQL statements. You can insert the target SQL Insert into the current SQL Console. Additionally, you can Edit or Delete the target SQL. : Favorites: View saved SQL statements. You can insert the target SQL Insert into the current SQL Console. Additionally, you can Edit or Delete the target SQL. : History: View the execution history of SQL on the target data source. You can choose to filter out the execution history of a certain time period or search the execution history by keywords (SQL statement, database name, error message). : History: View the execution history of SQL on the target data source. You can choose to filter out the execution history of a certain time period or search the execution history by keywords (SQL statement, database name, error message). : Settings : Settings- Keep Threads (MySQL only): Enable this feature to ensure that the current SQL Console maintains a continuous connection with the data source without establishing a new connection. It is suitable for scenarios that require session persistence, such as passing parameters or storing intermediate results in a series of queries.
- Results: Choose Overwrite or Append.
- Overwrite (default): The new result set will overwrite the previous execution result.
- Append: Generate a new tab to display the new result set.
- Theme: Change the theme of the SQL Console, choose between Light and Dark.
- Font Size: Drag the slider to adjust the font size of SQL statements in the SQL Console. The default values are as follows:
 : View Threads (MySQL, ClickHouse, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, OceanBase Oracle): Display information about all active connections on the current database server and the queries being executed by these connections. View Threads also supports automatic refresh functionality, with options to automatically refresh every 5, 10, 20, or 30 seconds. : View Threads (MySQL, ClickHouse, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, OceanBase Oracle): Display information about all active connections on the current database server and the queries being executed by these connections. View Threads also supports automatic refresh functionality, with options to automatically refresh every 5, 10, 20, or 30 seconds. : Enable Admin Mode|Disable Admin Mode Only Administrator can operate. After enabling this mode, all SQL executed in the SQL Console will not be subject to standardization or approval flows and can be executed directly. : Enable Admin Mode|Disable Admin Mode Only Administrator can operate. After enabling this mode, all SQL executed in the SQL Console will not be subject to standardization or approval flows and can be executed directly. : Import Demo Dataset Generate a test dataset in the current data source (only supported in test data sources). : Import Demo Dataset Generate a test dataset in the current data source (only supported in test data sources). : Logical E-R diagram (MySQL and OceanBase MySQL only) View the logical E-R diagram of the current database. : Logical E-R diagram (MySQL and OceanBase MySQL only) View the logical E-R diagram of the current database. : Full Screen Display the SQL Console in full screen (browser size). After going full screen, click : Full Screen Display the SQL Console in full screen (browser size). After going full screen, click  Exit to restore the original SQL Console size. Exit to restore the original SQL Console size. : AI Diagnosis opens the ChatDBA window on the far right of the SQL Console, allowing for knowledge base retrieval while writing SQL or viewing the history of AI diagnoses. : AI Diagnosis opens the ChatDBA window on the far right of the SQL Console, allowing for knowledge base retrieval while writing SQL or viewing the history of AI diagnoses.
|
| 7 | Search | Search for the object name, select the object on the left, and then search for the corresponding object name on the right. This supports databases, tables, columns, views, functions, stored procedures, triggers, and events. Currently, object search supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, DAMENG. For other data sources, you can input the table name to quickly locate the target data table. |
| 8 | Database list | Display all databases and tables in the current data source. The supported functionalities vary depending on the type of data source:MySQL|OceanBase|PolarDB-X|PolarDB MySQL|AnalyticDB MySQL|TDSQL-C MySQL|GaussDB for MySQL|Aurora MySQL|GaiaDB|GaiaDB-X|GreatSQL | MariaDB- Create Database: Right-click any database, click Create Database, enter the Name, Character, and Collation in the pop-up dialog box, click OK to visually create a database.
- Convert Schema: Right-click the target table, click Convert Schema to convert the current table's DDL statement into DDL statements for various database types using AI.
- Generate Code: Right-click the target table, click Generate Code to convert the current table structure into code for various programming languages using AI.
- Convert To (AI): Right-click the target stored procedure or function, click Convert To (AI) > Programming Language to convert the current stored procedure or function into code for the target programming language using AI. Supported languages: Java, Python, C#, C++, Golang, Rust, NodeJS.
- Add Table Notes For AI (MySQL only): Right-click on the target database, table, or column, and click Add Table Notes For AI to add comments to the target table and fields. For more information, please refer to Chat2SQL.
- Create Table: Right-click the target database or any table in the database, click Create Table to visually create a data table. For more information, see Designing MySQL Table Structures.
- Alter Table: Right-click the target table, click Alter Table to edit the structure of the target table. For more information, see Designing MySQL Table Structures.
- Create Non-Table Objects: Right-click on the target database, select Create Object > Non-Table Object Name to visually create non-table objects. Supported non-table objects include views, stored procedures, triggers, events, and functions. For more information, see Creating Non-Table Objects in MySQL Visually.
- Manage Non-Table Objects: Right-click on the name of the non-table object under the target database to execute operations such as create, edit, rename, copy, and delete for non-table objects. Supported non-table objects include views, stored procedures, triggers, events, and functions.
- Export: Right-click the target database or table, click Export to export the data table in various formats.
- Import: Right-click the target database or table, click Import to import data into the target database table using various methods.
- View Users: Right-click the User at the bottom of the database list, click View Users to view all user information in the current data source.
Oracle|OceanBase Oracle |DaMeng- Convert Schema: Right-click the target table, click Convert Schema to convert the current table's DDL statement into DDL statements for various database types using AI.
- Generate Code: Right-click the target table, click Generate Code to convert the current table structure into code for various programming languages using AI.
- Convert To (AI): Right-click the target function, click Convert To (AI) > Programming Language to convert the current stored procedure or function into code for the target programming language using AI. Supported languages: Java, Python, C#, C++, Golang, Rust, NodeJS.
SQL Server- Convert Schema: Right-click the target table, click Convert Schema to convert the current table's DDL statement into DDL statements for various database types using AI.
- Generate Code: Right-click the target table, click Generate Code to convert the current table structure into code for various programming languages using AI.
- Convert To (AI): Right-click the target stored procedure or function, click Convert To (AI) > Programming Language to convert the current stored procedure or function into code for the target programming language using AI. Supported languages: Java, Python, C#, C++, Golang, Rust, NodeJS.
ClickHousePostgreSQL|Greenplum|Klustron|DWS|openGauss|GaussDB| Vastbase- Create Database: Right-click any database, click Create Database, and enter the required parameters in the pop-up dialog box, then click OK to visually create a database.
- Create Schema: Right-click the target database or any schema, click Create Schema to visually create a schema.
- Edit Schema: Right-click on any schema, click Edit Schema to visually edit a schema.
- Add Table Notes For AI (PostgreSQL, Vastbase): Right-click on the target database, table, or column, and click Add Table Notes For AI to add comments to the target table and fields. For more information, please refer to Chat2SQL.
- Create Table (PostgreSQL, Greenplum, Vastbase): Right-click the target library, Schema, or any table in the library, click Create Table, you can visually create a data table. For more information, please see Designing PostgreSQL Table Structure.
- Alter Table (PostgreSQL, Vastbase): Right-click the target table, click Alter Table, you can edit the structure of the target table. For more information, please see Designing PostgreSQL Table Structure.
- Create Role: Right-click Login/Group Roles or the target role, click Create Role, enter the required parameters in the pop-up dialog box, then click OK to visually create a role.
- Edit Role: Right-click the target role, click Edit Role to visually edit the role.
TiDB- Create Database: Right-click any database, click Create Database, in the popped-up dialog box, enter Name, Character, and the corresponding Collation, click OK, to visually create the database.
- Create Table: Right-click the target database or any table in the database, click Create Table, to visually create the table.
- Alter Table: Right-click the target table, click Alter Table, to edit the structure of the target table.
Lindorm- Export: Right-click the target database or table, click Export to export the data table in various formats.
- Import: Right-click the target database or table, click Import to import data into the target database table using various methods.
Common Functions- Database Details or Schema Details: Right-click on the target database or Schema, click on Database Details or Schema Details to open the Database Details or Schema Details page. Here you can view details of the target database (PostgreSQL, KingBase, Klustron, GBase is currently not supported).
- Select Rows: Right-click the target table, click Select Rows to automatically query the data in the table. By default, it returns 100 rows.
- Table Details: Right-click the target table, click Table Details to open the Table Details page. You can view all the Columns, Indexes, and Triggers of the target table (GBase is currently not supported).
- Select Rows: Right-click the target view, click Select Rows to automatically query the data in the view. By default, it returns 100 rows.
- Generate DDL: Right-click the target object, click Generate DDL to generate the SQL statement for creating the object (not supported for some object types depending on the data source).
- Duplicate Query: Open a SQL Console for the current data source.
- Refresh: Right-click any object, click Refresh to refresh the database list.
- View Object Details: Hover the mouse over the target table name, column name, or index name to display the corresponding detailed information.
|
| 9 | SQL editor | The following features are supported:- SQL Execution: Supports single statement or batch execution.
- Chat2SQL (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Vastbase): Type / in the editor to enable Chat2SQL mode. With concise natural language input, you can quickly convert it into SQL statements. For more information, refer to Chat2SQL.
- Interrupt Execution: Click Stop to interrupt the execution of SQL during execution.
- Syntax Highlighting: Different syntax elements are displayed in different colors to improve code readability.
- SQL IntelliSense: Automatically pops up suggestions based on the semantics you enter while typing commands.
- View SQL Syntax Help: After entering an SQL keyword, select the keyword and right-click >Help to view the corresponding help information.
- SQL Templates: Provides common templates for CREATE, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements, etc. You only need to enter the preceding command to select the corresponding template. For example: entering CREATE allows you to choose CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, etc. templates.
- Right-click Menu:
- Execute: Execute the SQL statement at the cursor position.
- Format: Adjust the structure of the selected SQL statement to enhance readability.
- SQL Optimize: AI intelligently analyzes the SQL statement on the cursor line and provides optimization suggestions.
- Execution Plan: View the execution plan of the selected SQL statement.
- Favorite this SQL: Save all SQL statements in the current SQL Console to the SQL list for easy access next time.
- Favorites: View saved SQL statements. You can insert the target SQL Insert into the current SQL Console. Additionally, you can Edit or Delete the target SQL.
- History: View the execution history of SQL on the target data source. You can choose to filter out the execution history of a certain time period or search the execution history by keywords (SQL statement, database name, error message).
- View Threads: Display information about all active connections on the current database server and the queries being executed by these connections. View Threads also supports automatic refresh functionality, with options to automatically refresh every 5, 10, 20, or 30 seconds.
- General Operations: Including Cut, Copy, Paste, and Select All.
- Select Current SQL: Select the SQL statement at the cursor position.
- Help: AI analyzes the currently selected content to provide information such as the semantics of the target SQL syntax, the definition of the target table's table structure, and an overall explanation of the SQL statement logic.
|
| 10 | Execution information and result set | Display execution information and result set for SQL query.- Execution Information: Includes execution time, executed SQL statement, execution status, execution duration, and other details. When an execution error occurs, a AI Diagnosis button is provided. Clicking AI Diagnosis opens the ChatDBA window on the right side, where ChatDBA will perform a detailed analysis of the error cause and provide actionable recommendations.
- Result Set: Displays the returned results of the SQL query. You can perform the following actions:
Edit Result Set (Conditions: Single table query, includes primary key column or unique key column)- Click Add, Delete, or modify data directly: You can visually perform insert, delete, and update operations on the database.
- Edit Row: Right-click on the target cell, select Edit Row, and edit all fields in the row of the cell.
- Upload File: Right-click on the target cell, select Upload File, and upload a file to fill the current cell.
- Paste Row: Right-click on the target cell, select Paste Row, and paste copied row information over the current row.
- Paste Field: Right-click on the target cell, select Paste Field, and overwrite the current cell with the information from the clipboard.
- Set to Null: Right-click on the target cell, select Set to Null, and set the current cell to NULL (only available if the field is not set as NOT NULL).
- Set to Empty String: Right-click on the target cell, select Set to Empty String, and set the cell to an empty value.
- Delete Row: Right-click on the target cell, select Delete Row, and delete the row containing the current cell.
Common Actions- Click
 : Display the result set in column mode. : Display the result set in column mode. - Click
 : Display the result set in row mode. : Display the result set in row mode. - Click
 > Export Result: Supports exporting data tables in various formats, with the export range being either the current page or all data (up to 10,000 entries). > Export Result: Supports exporting data tables in various formats, with the export range being either the current page or all data (up to 10,000 entries). - Click
 > Create export task: Supports quickly creating data export tasks in the current window. The default export scope is the current result set, eliminating the need to switch to the Data Export module. > Create export task: Supports quickly creating data export tasks in the current window. The default export scope is the current result set, eliminating the need to switch to the Data Export module. - Click
 : Scrolls the result set to the bottom of the page. Clicking : Scrolls the result set to the bottom of the page. Clicking  restores the view. restores the view. - Click
 : Allows operations like locking, hiding, and showing columns in the result set. : Allows operations like locking, hiding, and showing columns in the result set. - Result set search: Supports Fuzzy and Exact.
- Click the small arrow on the right side of column names to sort the result set.
- Copy Row: Right-click on the target cell, select Copy Row, and copy the entire row of the cell.
- Copy Column: Right-click on the target cell, select Copy Column, and copy the entire column of the cell.
- Copy Field: Right-click on the target cell, select Copy Field, and copy the current cell.
- Copy as: Right-click on the target cell, select Copy as, and choose to copy the row data in multiple formats.
- Export: Right-click on any cell, select Export, and export the current result set in various formats, exporting the current page or all data (up to 10000 rows).
- View SQL Statement Corresponding to Result Set: Hover over the tab of the target result set to display the SQL statement corresponding to that result set.
- View Field Details: Hover the mouse over the target field to display its name, data type, length, and comment information.
- Single-Column Search: Click the
 icon to the right of the target column name, then enter a keyword in the pop-up text box to filter and search within that column. icon to the right of the target column name, then enter a keyword in the pop-up text box to filter and search within that column.
|
 For details on how to use the SQL console, please refer to the SQL console interface introduction .tip
For details on how to use the SQL console, please refer to the SQL console interface introduction .tip