Debugging Stored Procedures
NineData's stored procedure debugging feature provides visual execution and debugging capabilities. It supports setting breakpoints, single-step execution, variable monitoring, and exception catching, helping users quickly identify and resolve issues in the design and functional implementation of stored procedure objects.
Background Information
In enterprise applications, databases are not only the center of data storage but also carry a large amount of complex business logic, such as data validation, batch processing, statistical calculations, etc. These logics are usually implemented through stored procedures, functions, and packages. However, traditional debugging methods have the following pain points:
- The need to manually write PL/SQL debugging scripts, which is cumbersome and prone to errors.
- Unable to intuitively see variable values, call stacks, and DBMS outputs during the execution process.
- Difficult exception capturing, and time-consuming problem location.
The stored procedure debugging feature is designed to solve these problems. With a visual debugging tool, users can develop, test, and maintain database logic more efficiently.
Feature Introduction
NineData's stored procedure debugging feature is used for visual execution and debugging of stored procedures (Procedure), functions (Function), and packages (Package) in the database, greatly simplifying the problem location and repair process for database developers and operators in complex business logic.
- Executable: Supports direct calling of stored procedures or functions, and viewing return results or output information.
- Debuggable: Supports debugging operations such as breakpoint setting, step-by-step execution, variable value viewing, and exception capturing.
Usage Scenarios
Verification of newly developed stored procedures: After the stored procedure is written, use the debugging feature to execute step by step to confirm the correctness of the logic.
Quick location of production issues: When exceptions occur in the production environment, the execution process can be restored through the debugging feature to quickly find the root of the problem.
Logic optimization and performance debugging: Step-by-step debugging of stored procedures that run slowly or have inaccurate results, analyzing bottlenecks or logical defects.
Prerequisites
In the commercial versions (DevOps Pro, DevOps Enterprise), please ensure that your monthly/yearly subscription is not expired, as it may result in the inability to use the Database DevOps service. You can quickly check the remaining quota and expiration date at the top right corner of the NineData console page.
- The data source type used is Oracle, PostgreSQL.
- Sufficient database permissions (execution, debugging, viewing object definitions, etc.).
Operation Steps
In the navigation tree on the left side of the SQL Console, expand the target non-table object (stored procedure|function|package).
Right-click on the target non-table object and click Debug Procedures|Debug Function|Debug Package to jump to the debugging page.
tip- If you do not find the debugging option in the right-click menu, please confirm that your target non-table object has been compiled.
- Non-table objects that have not passed compilation will be marked with a red exclamation mark. You can hover the mouse over the red exclamation mark to view the specific error information, fix the error, and try again.
- The right-click menu provides a compile object feature. For errors that are not due to the non-table object itself, you can re-verify through the compile button after fixing.
You can perform the following operations on the debugging page:
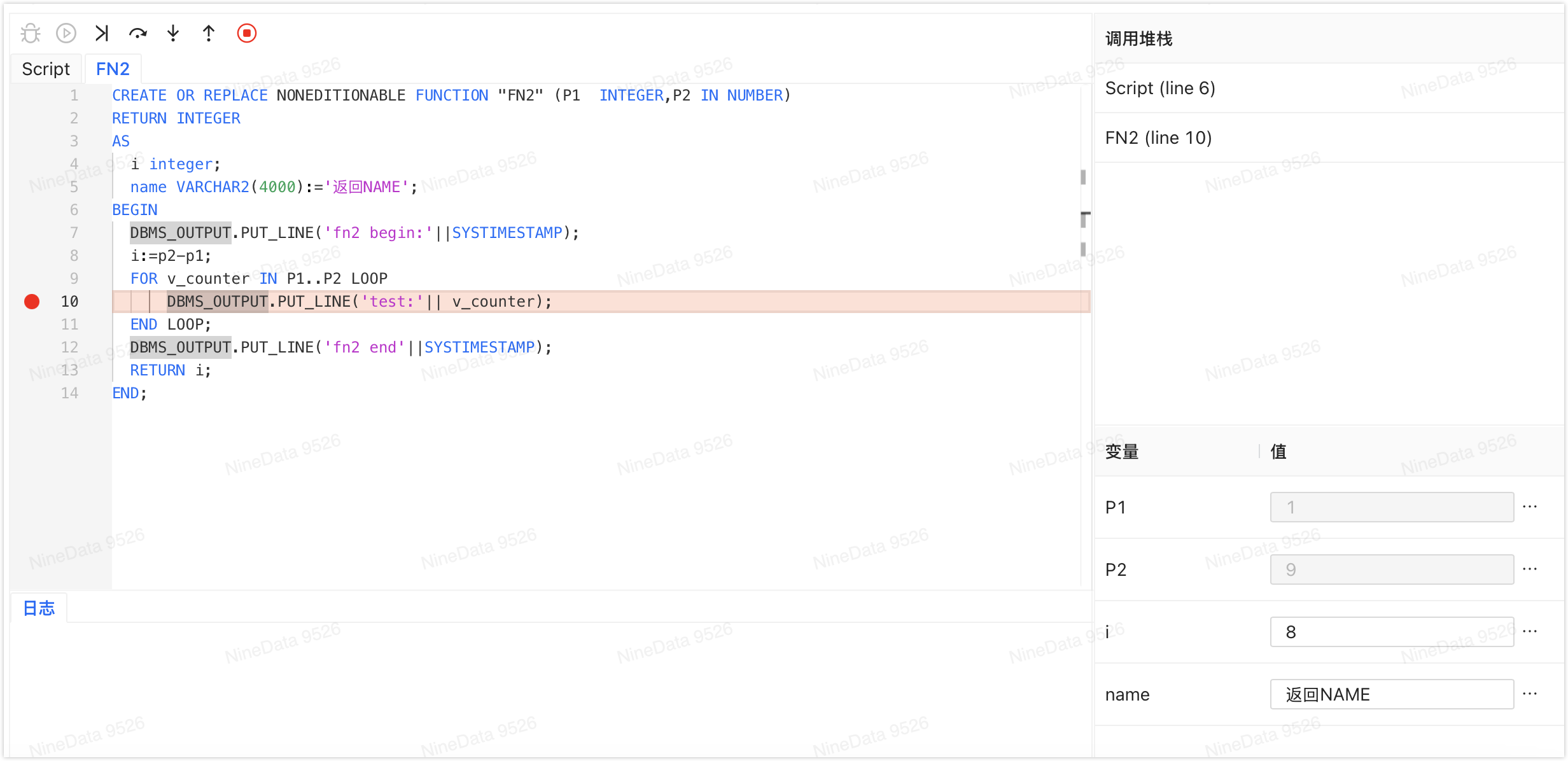
Operation Description Debug
Begin the debugging session and input initial test variable values. Start
Run the code, supporting breakpoint pause. Resume
Retreat to the beginning of debugging. Step Over
Execute the current line without entering the sub-process/ function. Step Into
Execute the current line and enter the called sub-process/ function. Step Out
Execute the current sub-process/ function and return to the upper layer. Stop
Stop debugging. View Variables During the debugging process, you can view or modify variable values in real-time in the Variables View Logs (DBMS Output) After running the entire debugging process, you can view the DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINEoutput content in the Logs area.