MySQL to Elasticsearch
NineData data replication supports replicating data from MySQL to Elasticsearch, enabling Elasticsearch to search and analyze MySQL data.
Background Information
Elasticsearch is a popular distributed search and analytics engine used for processing large volumes of data and providing real-time search and analytics capabilities, including full-text search, auto-completion, aggregation, geospatial search, and machine learning. Replicating data from MySQL to Elasticsearch provides better search performance, powerful analytics and aggregation capabilities, and helps to further explore the value of your data.
Prerequisites
The source and target data sources have been added to NineData. For information on how to add them, please see Creating a Data Source.
The source database type is MySQL or a MySQL-compatible database, such as MySQL, MariaDB, PolarDB MySQL, TDSQL-C, GaussDB MySQL, etc.
The target database type is Elasticsearch version 8.7, 7.0, 6.0, or 5.0.
The source data source must have Binlog enabled, and the following Binlog-related parameters must be set:
binlog_format=ROWbinlog_row_image=FULL
tipIf the source data source is a standby database, to ensure that the complete Binlog log is obtained, the
log_slave_updatesparameter also needs to be enabled.
Procedure
NineData’s data replication product has been commercialized. You can still use 10 replication tasks for free, with the following considerations:
Among the 10 replication tasks, you can include 1 Incremental task, with a specification of Micro.
Tasks with a status of Terminated do not count towards the 10-task limit. If you have already created 10 replication tasks and want to create more, you can terminate previous replication tasks and then create new ones.
When creating replication tasks, you can only select the Spec you have purchased. Specifications that have not been purchased will be grayed out and cannot be selected. If you need to purchase additional specifications, please contact us through the customer service icon at the bottom right of the page.
Log in to the NineData Console.
Click Replication > Data Replication in the left navigation pane.
On the Replication page, click the Create Replication button in the upper right corner.
On the Source & Target tab, configure the parameters in the following table and click Next.
Parameter Description Name Enter the name of the data synchronization task. To facilitate subsequent searching and management, please use a meaningful name of no more than 64 characters. Source The data source of the object to be synchronized. Select the MySQL data source where the data to be copied is located. Target The data source that receives the synchronized object. Select the target Elasticsearch data source. Index Name After data is migrated from MySQL to Elasticsearch, Elasticsearch adds indexes to make the management and querying of this data more convenient. You can choose the naming method for these indexes here. - TableName (default): Use the table name of the original MySQL table directly. For example, if an index named "users" is created, it can be understood that the documents stored in this index have a structure similar to that of the "users" table.
- DbNameTbName: Use the format of `[original database name][original table name]` as the naming convention. For example, if an index named "mydb_users" is created, it can be understood that the documents stored in this index belong to the "users" table in the "mydb" database.
Type - Schema: Synchronize the database and table structure of the source data source.
- Full: Synchronize all objects and data of the source data source, that is, full data replication.
- Incremental: After the full synchronization is completed, perform incremental synchronization based on the log of the source data source. Click the
icon to uncheck certain operation types according to your needs. Once unchecked, these operations will be ignored during incremental synchronization.
Target Table Preparation - If target table already exists (select whenSchema is selected)
- Pre-Check Error and Stop Task: Stop the task when a table with the same name is detected during the pre-check stage.
- Skip and Continue Task: Send a prompt when a table with the same name is detected during the pre-check stage and continue the task. When replicating the structure, ignore the table with the same name. If you also replicate data, the data will be appended to the table with the same name without overwriting the original data.
- Delete Objects and Rewrite: Send a prompt when a table with the same name is detected during the pre-check stage and continue the task. When replicating the structure, delete the table with the same name in the target database and replicate the table structure based on the source database. If you also replicate data, the data will be written after the table structure replication is complete.
- Keep Schema and Clear Data, then Rewrite (optional when replicating both structure and data): Send a prompt when a table with the same name is detected during the pre-check stage and continue the task. When replicating the structure, the table structure in the target database is retained, and the data in the table with the same name is cleared before being replicated from the original table.
- Target Table Exists Data (select whenSchema is not selected)
- Pre-Check Error and Stop Task: Stop the task when data is detected in the target table during the pre-check stage.
- Ignore the existing data and append : Ignore the data in the target table when it is detected during the pre-check stage and append and write other data.
- Clear the existing data before write: Delete the conflicting data in the target table when it is detected during the pre-check stage and write it again.
- Dynamic Desensitization (currently only supported for MySQL to MySQL): After being enabled, data in the source data source that has sensitive columns configured is copied to the target data source in a desensitized form to ensure the security of sensitive data.
On the Objects tab, configure the following parameters, and then click Next.
Parameter Description Replication Objects Select the content to be copied. You can select Full Instance to copy all content in the source database, or select Customized Object, select the content you want to copy in the Source Object list, and click >Add to the rightTarget Object list. On the Mapping tab, you can configure each table that needs to be copied to Elasticsearch, as well as each field in the table. By default, all tables and fields of the selected database will be copied. At the same time, you can customize the configuration of DOC ID for each index. DOC ID is the unique identifier for each document in Elasticsearch, and is used to retrieve, update or delete the document. You can specify it yourself or let Elasticsearch generate it, and this ID is unique in the same index., or leave it blank for Elasticsearch to generate.
tipYou can click Mapping & Filtering on the right side of the page to customize the name of the fields after they are synchronized to Elasticsearch. In addition, you can set Data Filter so that only data that meets the filtering conditions will be synchronized to Elasticsearch.
On the Pre-check tab, wait for the system to complete the pre-check. After the pre-check is passed, click Launch.
tip- If the pre-check fails, you need to click the Details button on the right side of the target check item in the Actions column, troubleshoot the cause of the failure, manually fix it, and then click Check Again to perform the pre-check again until it passes.
- The check items with Warning in Result can be repaired or ignored depending on the specific situation.
On the Launch page, after being prompted that the task has started successfully, the synchronization task starts running. At this time, you can perform the following operations:
- Click View Details to view the execution status of each stage of the synchronization task.
- Click Back to list to return to the Replication task list page.
View Synchronization Results
Log in to the NineData Console.
Click Replication > Data Replication in the left navigation pane.
On the Replication page, click the target.
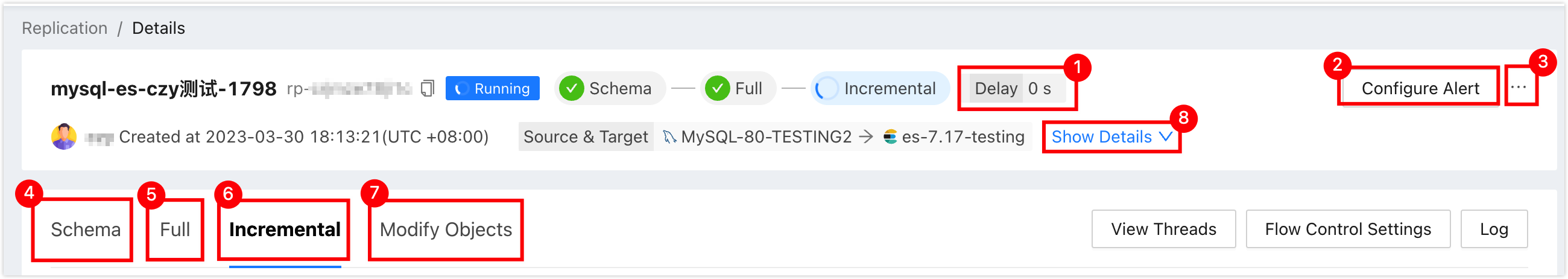
No. Function Description 1 Sync delay The data synchronization delay between the source and target data sources. 0 seconds means no delay between the two ends, which means that the data on the Kafka end has caught up with the MySQL end. 2 Alert configuration After configuring the alert, the system will notify you in the way you choose when the task fails. For more information, please see Introduction to operation and maintenance monitoring. 3 More - Pause: Pause the task. Only tasks with a status of Running can be selected.
- Terminate: Terminate tasks that are incomplete or listening (i.e., in incremental synchronization). After terminating the task, the task cannot be restarted, so please proceed with caution.
- Delete: Delete the task. Once the task is deleted, it cannot be restored, so please proceed with caution.
4 Structure replication (displayed in scenarios involving structure replication) Displays the progress and detailed information of structure replication. - Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of structure replication.
- Click on : View the latest information.
5 Full replication (displayed in scenarios involving full replication) Displays the progress and detailed information of full replication. - Click on Monitor on the right side of the page: View various monitoring indicators during full replication. During full replication, you can also click on Flow Control Settings on the right side of the monitoring indicator page to limit the rate at which data is written to the target data source. The unit is MB/s.
- Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of full replication.
- Click on the icon on the right side of the page: View the latest information.
6 Incremental replication (displayed in scenarios involving incremental replication) Displays various monitoring indicators of incremental replication. - Click on View Threads on the right side of the page: View the operations currently being performed by the current replication task, including:
- Thread ID: The current thread number of the replication task which is executed in multiple threads.
- Execute SQL: Details of the SQL statement currently executing in the thread.
- Response Time: The response time of the current thread. If this value increases, the current thread may be stuck due to some reason.
- Event Time: The timestamp when the current thread was started.
- Status: The status of the current thread.
- Click on Flow Control Settings on the right side of the page: Limit the rate at which data is written to the target data source. The unit is rows/s.
- Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of incremental replication.
- Click on the icon on the right side of the page: View the latest information.
7 Modify object Displays the modification records of the synchronized object. - Click on Modify Objects on the right side of the page to configure the synchronization object. .
- Click on the icon on the right side of the page: View the latest information.
8 Expand Displays detailed information about the current replication task, including Type, Replication Objects, Started, etc.
Appendix 1: Mapping table of MySQL and Elasticsearch data types during data replication.
During the data replication process, MySQL data types are mapped to corresponding Elasticsearch data types.
| Category | MySQL Data Type | ElasticSearch Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| Numeric | TINYINT | Short |
| TINYINT UNSIGNED | ||
| SMALLINT | Integer | |
| SMALLINT UNSIGNED | ||
| MEDIUMINT | ||
| MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | ||
| INT | ||
| INT UNSIGNED | ||
| BIGINT | Long | |
| BIGINT UNSIGNED | ||
| BIT(M) | Uint64 | |
| Decimal | Decimal(10, 0) | |
| Numeric | ||
| Decimal(P, S) | Decimal(P, S) | |
| Float | Float32 | |
| Double | Float64 | |
| BOOL, BOOLEAN | 21.12 or later: Boolean Before 21.12: Int8 | |
| DATE AND TIME | DATE | Date |
| DATETIME[(fsp)] | ||
| Timestamp[(fsp)] | ||
| Time[(fsp)] | ||
| YEAR[(4)] | ||
| STRING | CHAR/VARCHAR | Text |
| TINYTEXT/TEXT/MEDIUMTEXT/LONGTEXT | ||
| BINARY/VARBINARY | Binary | |
| TINYBLOB/BLOB/MEDIUMBOLB/LONGBLOB | ||
| ENUM | Keyword | |
| SET | ||
| JSON | JSON | Object |
| SPATIAL | POINT | Geo_point |
| LINESTRING | Geo_shape | |
| POLYGON | ||
| MULTIPOINT | ||
| MULTILINESTRING | ||
| MULTIPOLYGON | ||
| GEOMETRYCOLLECTION GEOMCOLLECTION | ||
| GEOMETRY |
Appendix 2: Checklist of Pre-Check Items
| Check Item | Check Content |
|---|---|
| Source Data Source Connection Check | Check the status of the source data source gateway, instance accessibility, and accuracy of username and password |
| Target Data Source Connection Check | Check the status of the target data source gateway, instance accessibility, and accuracy of username and password |
| Target Database Permission Check | Check if the account permissions in the target database meet the requirements |
| Source Database Permission Check | Check if the account permissions in the source database meet the requirements |
| Check if Source Database log_slave_updates is Supported | Check if log_slave_updates is set to ON when the source database is a slave |
| Source Data Source and Target Data Source Version Check | Check if the versions of the source database and target database are compatible |
| Check if Source Database is Enabled with Binlog | Check if the source database is enabled with Binlog |
| Check if Source Database Binlog Format is Supported | Check if the binlog format of the source database is 'ROW' |
| Check if Source Database binlog_row_image is Supported | Check if the binlog_row_image of the source database is 'FULL' |
| Target Database Data Existence Check | Check if data exists for the objects to be replicated in the target database |