Migrating and Synchronizing TiDB to PostgreSQL
NineData replication supports copying data from TiDB to PostgreSQL, including structure and full data replication.
Feature Introduction
NineData data replication supports high-performance replication of structure, full data, and incremental data between data sources. For certain data sources, it also provides bidirectional replication, enabling the quick construction of geo-distributed active-active business architectures.
- Structure: Supports the replication of object structures between homogeneous and heterogeneous data sources, greatly reducing the barrier to data replication between two sources.
- Full Data: Achieves row-level concurrent batch replication through intelligent data sharding, effectively ensuring replication performance. The independently developed novel breakpoint resume technology ensures the accuracy of data in tables without primary keys.
- Incremental Data: Supports DML and DDL incremental data replication for all object types. By leveraging technologies such as row-level concurrency and hotspot merging, it delivers robust replication performance.
- Bidirectional Real-time Data Replication (only between MySQL instances): Direct bidirectional replication of data between multiple nodes ensures that all node data remains up-to-date.
With the above features, it is easy and efficient to achieve scenarios such as full|incremental data replication, full|incremental data migration, full|incremental data synchronization, data integration, and seamless migration without downtime, providing enterprises with flexible and reliable data replication solutions.
Prerequisites
The source and target data sources have been added to NineData. For instructions on how to add data sources, please refer to Adding Data Sources.
You have the following permissions for the source and target data sources.
Replication Type Source Data Source Target Data Source Structure Replication SELECT、SHOW VIEW DDL Full Data Replication SELECT、SHOW VIEW DML
Usage Limitations
- Before performing data synchronization, it is necessary to assess the performance of the source and target data sources, and it is recommended to perform data synchronization during off-peak business hours. Otherwise, the initial full data will occupy a certain amount of read and write resources of the source and target data sources, leading to increased database load.
- It is recommended to ensure that each table in the synchronization object has a primary key or unique constraint, and the column names are unique, otherwise, the same data may be synchronized repeatedly.
- The Enterprise Edition (Exclusive Cluster) of NineData supports incremental data replication from TiDB as the source. To enable this feature, you need to activate the TiCDC Service within the same internal network environment to collect incremental logs. NineData will then read these incremental logs from the TiCDC service to achieve incremental replication.
Operation Steps
NineData’s data replication product has been commercialized. You can still use 10 replication tasks for free, with the following considerations:
Among the 10 replication tasks, you can include 1 Incremental task, with a specification of Micro.
Tasks with a status of Terminated do not count towards the 10-task limit. If you have already created 10 replication tasks and want to create more, you can terminate previous replication tasks and then create new ones.
When creating replication tasks, you can only select the Spec you have purchased. Specifications that have not been purchased will be grayed out and cannot be selected. If you need to purchase additional specifications, please contact us through the customer service icon at the bottom right of the page.
Log in to the NineData Console.
Click on Replication in the left navigation bar.
On the Replication page, click on Create Replication in the top right corner.
On the Source & Target tab, configure according to the table below and click on Next.
Parameter Description Name Enter the name of the data synchronization task. To facilitate subsequent search and management, please use a meaningful name as much as possible. Up to 64 characters are supported. Source The data source where the synchronization object is located. Target The data source that receives the synchronization object. Target DB Select which database to synchronize the data to the target. Type Choose the content that needs to be copied to the target data source. - Schema: Only synchronize the database table structure of the source data source, without synchronizing the data.
- Full: Synchronize all objects and data of the source data source, that is, full data replication. The switch on the right is the switch for periodic full data replication, more information, please refer to Periodic Full Data Replication.
If target table already exists(Required when Schema is selected) - Pre-Check Error and Stop Task: Stop the task when the same name table is detected during the pre-inspection phase.
- Skip and Continue Task: Send a prompt and continue the task when the same name table is detected during the pre-inspection phase. During structure replication, ignore the same name table. If you also perform data replication, the data will be appended in the same name table without overwriting the original data.
- Delete Objects and Rewrite: Send a prompt and continue the task when the same name table is detected during the pre-inspection phase. During structure replication, delete the same name table in the target database and re-copy the table structure based on the source database. If you also perform data replication, the data will be written after the table structure replication is completed.
- Keep Schema and Clear Data, then Rewrite(Optional when both structure and data replication are performed): Send a prompt and continue the task when the same name table is detected during the pre-inspection phase. During structure replication, retain the table structure in the target database, and clear the data in the same name table at the beginning of data replication, then re-copy from the original table.
Target Table Exists Data(Required when Schema is not selected) - Pre-Check Error and Stop Task: Stop the task when data is detected in the target table during the pre-inspection phase.
- Ignore the existing data and append : Ignore the data when it is detected in the target table during the pre-inspection phase, and append the other data.
- Clear the existing data before write: Delete the data when it is detected in the target table during the pre-inspection phase, and re-write it.
On the Objects tab, configure the following parameters, and then click on Next.
Parameter Description Replication Objects Select the content that needs to be copied. You can choose All Objects to copy all content from the source database, or you can choose Customized Object, select the content that needs to be copied in the Source Object list, and click > to add to the right Target Object list. If you need to create multiple replication chains with the same replication object, you can create a configuration file and import it when creating a new task. Click on Import Config in the top right corner, and then click on Download Template to download the configuration file template to the local, edit it and click on Upload to upload the configuration file to achieve batch import. Configuration file description:
Parameter Description source_table_nameThe source table name where the object to be synchronized is located. destination_table_nameThe target table name that receives the synchronized object. source_schema_nameThe source Schema name where the object to be synchronized is located. destination_schema_nameThe target Schema name that receives the synchronized object. source_database_nameThe source database name where the object to be synchronized is located. target_database_nameThe target database name that receives the synchronized object. column_listThe list of fields that need to be synchronized. extra_configurationAdditional configuration information can be set here: column_rules: Used to define column mapping and value rules. Field descriptions:column_name: Original column name.destination_column_name: Target column name.column_value: Value to assign, which can be an SQL function or a constant.
filter_condition: Used to specify row-level filtering conditions; only rows that meet the criteria will be copied.
tipAn example of the
extra_configurationcontent is as follows:{
"extra_config": {
"column_rules": [
{
"column_name": "created_time", // Original column name to map.
"destination_column_name": "migrated_time", // Target column name mapped to "migrated_time".
"column_value": "current_timestamp()" // Change the column value to the current timestamp.
}
],
"filter_condition": "id != 0" // Only rows where ID is not 0 will be synchronized.
}
}For a complete example of the configuration file, refer to the downloaded template.
On the "Mapping" tab, select different operations according to the selected replication type, and then click on Save and Pre-Check. Click on the drop-down menu on the right side of Object Owner to specify the owner of the object, if not selected, the default is An account with the same name as schema. If there are updates in the source and target data sources during the mapping configuration phase, you can click on the Refresh Metadata button in the top right corner of the page to re-acquire the information of the source and target data sources.
Including Schema: Configure the table name after the target table is synchronized to the target data source.
Not including Schema: The system defaults to selecting the same name database in the target data source, if it does not exist, you need to manually select the target library. The table name and column name in the target library need to be consistent with the synchronization object. If it is not consistent, you can also manually map the table name and column name.
You can click on the Mapping & Filtering on the right side of the page to customize the name of the column name synchronized to the target data source. In addition, you can also set Data Filter, configure filtering conditions through comparison expressions, only data that meets the filtering conditions will be synchronized to the target data source. For example, set the filtering condition to
emp_no>=10005, then the data in the emp_no column with a value less than 10005 will not be synchronized to the target data source.On the "Pre-check" tab, wait for the system to complete the pre-inspection, after the pre-inspection is passed, click on Launch.
tip- You can check Enable data consistency comparison. After the synchronization task is completed, automatically start the data consistency comparison based on the source data source to ensure that the data on both sides is consistent. According to the Type you selected, the start timing of Enable data consistency comparison is as follows:
- Schema: Start after the structure replication is completed.
- Schema+Full, Full: Start after the full data replication is completed.
- If the pre-inspection does not pass, you need to click on the Details in the Actions column on the right side of the target inspection item, troubleshoot the cause of the failure, manually repair it, and then click on Check Again to re-execute the pre-inspection until it passes.
- The Result is Warning inspection items, which can be repaired or ignored according to the specific situation.
- You can check Enable data consistency comparison. After the synchronization task is completed, automatically start the data consistency comparison based on the source data source to ensure that the data on both sides is consistent. According to the Type you selected, the start timing of Enable data consistency comparison is as follows:
On the Launch page, prompt Launch Successfully, the synchronization task starts to run. At this time, you can perform the following operations:
- Click on View Details to view the execution of each stage of the synchronization task.
- Click on Back to list to return to the Replication task list page.
Viewing Synchronization Results
Log in to the NineData Console.
Click on Replication > Data Replication in the left navigation pane.
On the Replication page, click on the Task ID of the target synchronization task, and the page description is as follows.
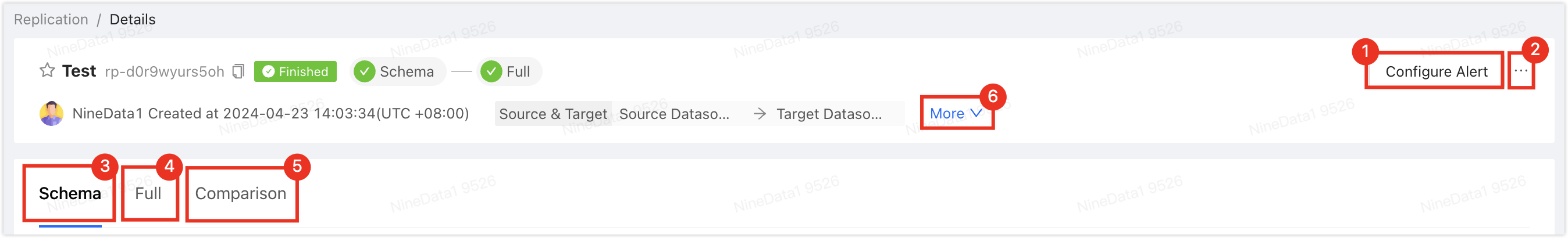
Number Function Description 1 Configure Alerts After configuring alerts, the system will notify you in the selected way when the task fails. For more information, please refer to Operational Monitoring Overview. 2 More - Pause: Pause the task. Only tasks with the status Running are selectable.
- Duplicate: Create a new replication task with the same configuration as the current task.
- Terminate: End tasks that are incomplete or in listening (i.e., in incremental synchronization). After terminating the task, it cannot be restarted, so please proceed with caution. If triggers are included in the synchronization object, trigger replication options will pop up, please choose as needed.
- Delete: Delete the task. Once the task is deleted, it cannot be recovered, so please proceed with caution.
3 Structural Replication (Displayed in scenarios involving structural replication) Display the progress and details of structural replication. - Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of structural replication.
- Click on
on the right side of the page: View the latest information.
- Click on View DDL in the Actions column on the right side of the target object in the list: View SQL playback.
4 Full Replication (Displayed in scenarios involving full replication) Display the progress and details of full replication. - Click on Monitor on the right side of the page: View various monitoring indicators during full replication. During full replication, you can also click on Flow Control Settings on the right side of the monitoring indicator page to limit the rate of data written to the target data source per second. The unit is rows/second.
- Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of full replication.
- Click on
on the right side of the page: View the latest information.
5 Data Comparison Display the comparison results between the source data source and the target data source. If you have not enabled data comparison, click Enable Comparison on the page. - Click on Re-compare on the right side of the page: Re-initiate the comparison of data between the current source and target ends.
- Click on Stop on the right side of the page: After starting the comparison task, you can click this button to stop the comparison task immediately.
- Click on Log on the right side of the page: View the execution log of consistency comparison.
- Click on Monitor (only displayed in data comparison): View the trend chart of RPS (records per second compared) for comparison. Click on Details to view records from earlier times.
- Click on
in the Actions column on the right side of the comparison list (displayed only under the Data tab when there is inconsistency): View detailed comparison between the source and target ends.
- Click on
in the Actions column on the right side of the comparison list (displayed only in case of inconsistency): Generate change SQL, which you can directly copy to the target data source to execute and modify the inconsistent content.
6 Expand Display detailed information of the current replication task. Common Options: - Export table configuration: Export the current task's database and table configuration, allowing for quick import when creating a new replication task. This helps rapidly establish multiple replication links with the same replication objects.
- Alert Rules: Configure the alarm strategy for the current task.
Appendix 1: Data Type Mapping Table
| Category | TiDB Data Type | PostgreSQL Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| Numeric | TINYINT | SMALLINT |
| TINYINT UNSIGNED | SMALLINT | |
| SMALLINT | SMALLINT | |
| SMALLINT UNSIGNED | INTEGER | |
| MEDIUMINT | INTEGER | |
| MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED | INTEGER | |
| INT | INTEGER | |
| INT UNSIGNED | BIGINT | |
| BIGINT | BIGINT | |
| BIGINT UNSIGNED | NUMERIC | |
| BIT(M) | BIT(N) | |
| DECIMAL() | NUMERIC | |
| NUMERIC | NUMERIC | |
| FLOAT | FLOAT | |
| DOUBLE | FLOAT | |
| BOOL, BOOLEAN | SMALLINT | |
| DATE AND TIME | DATE | DATE |
| DATETIME[(fsp)] | TIMESTAMP | |
| TIMESTAMP[(fsp)] | TIMESTAMPTZ | |
| TIME[(fsp)] | TEXT | |
| STRING | YEAR[(4)] | INTEGER |
| CHAR | CHAR | |
| VARCHAR | VARCHAR | |
| BINARY/VARBINARY | BYTEA | |
| TINYTEXT/TEXT/MEDIUMTEXT/LONGTEXT | TEXT | |
| TINYBLOB/BLOB/MEDIUMBLOB/LONGBLOB | BYTEA | |
| ENUM | VARCHAR | |
| SET | VARCHAR | |
| JSON | JSON | JSON |
Appendix 2: Pre-Check Item List
| Check Item | Check Content |
|---|---|
| Target Database Data Existence Check | Check if the data to be replicated already exists in the target database |
| Target Database Same Name Object Existence Check | Check if the object to be replicated already exists in the target database |
| Source Data Source Connection Check | Check the gateway status of the source data source, whether the instance is reachable, and the accuracy of the username and password |
| Target Data Source Connection Check | Check the gateway status of the target data source, whether the instance is reachable, and the accuracy of the username and password |