Create a PostgreSQL Data Source
NineData supports adding various types and environments of data sources to the console for unified management. You can use database DevOps, backup and recovery, data replication, and database comparison features for data sources that have been added. This article introduces how to add a PostgreSQL data source to NineData.
Prerequisites
The server IP address of NineData has been added to the data source allowlist. Please refer to the image below for instructions on how to obtain the server IP address.
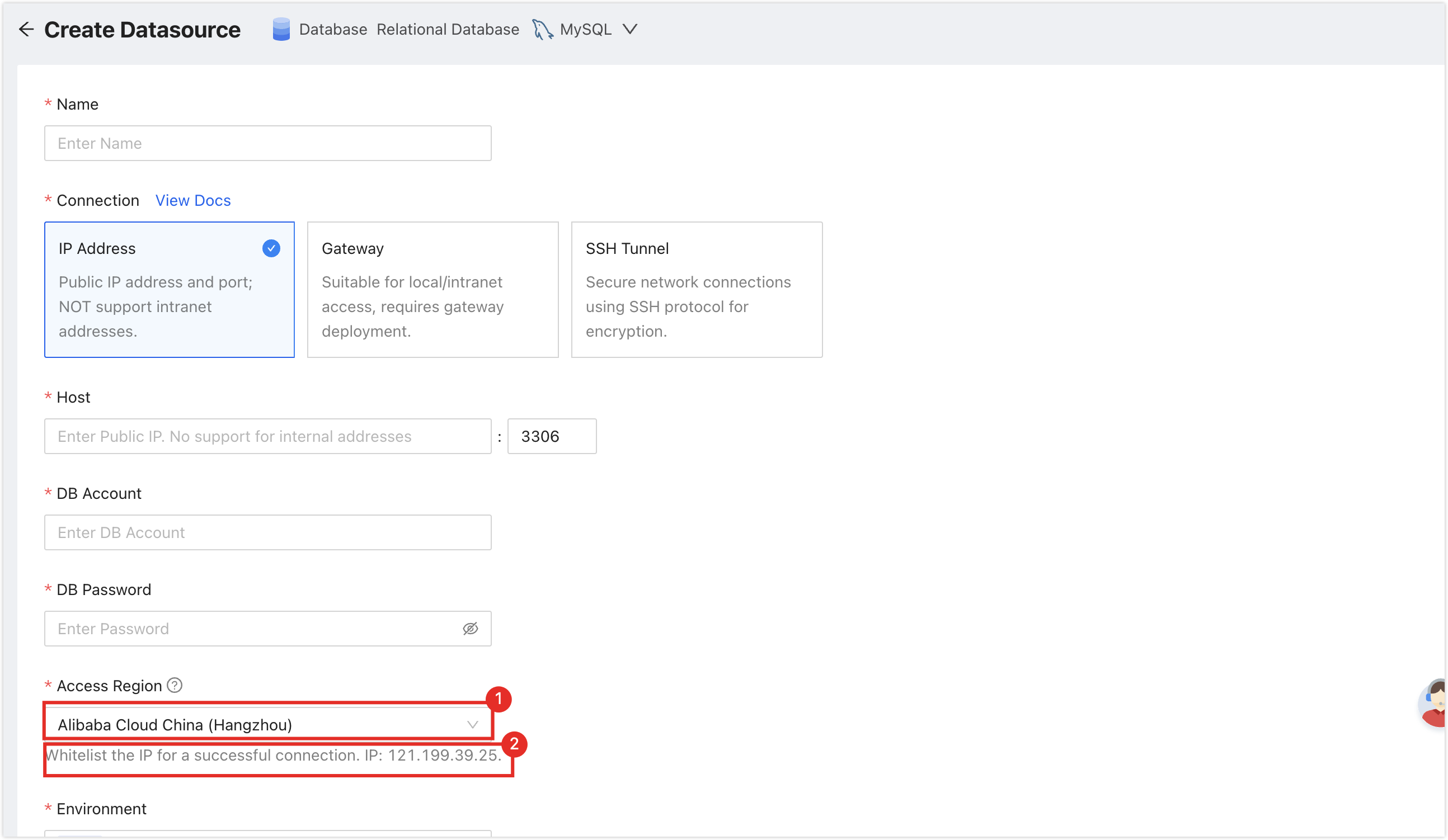
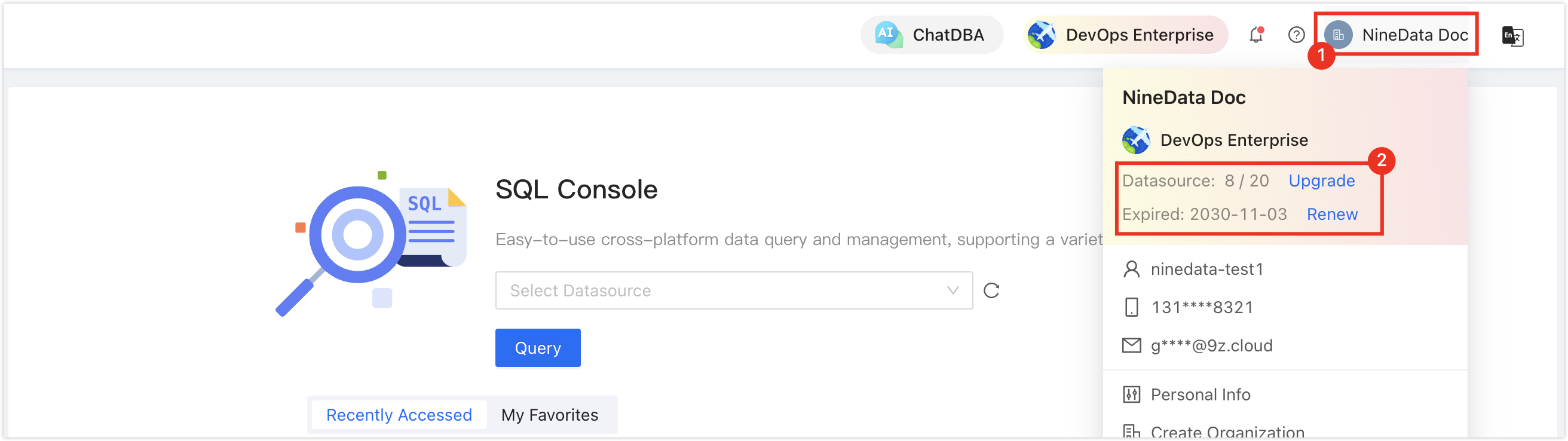
Make sure you have available data source quota; otherwise, the data source cannot be added. You can quickly check your remaining quota at the top-right corner of the NineData console.
Operation Steps
Log in to the NineData Console.
On the left navigation pane, click Datasource > Datasource.
- Click Datasource tab, and click Create Datasource on the page. In the popup window for selecting the data source type, choose Database > (the type of data source to be added), and configure the parameters based on the table below on the Create Datasource page.tip
If you make a mistake during the operation, you can click the
icon at the top of the Create Datasource page to make a new selection.
Configure the data source parameters:
Parameter Description Name Enter the name of the data source. To facilitate subsequent search and management, please use a meaningful name. Configuration items when Connection is IP Address Host: The public connection address and port of the data source. Configuration items when Connection is Gateway - Gateway: Select the NineData gateway installed on the host where the data source is located.
- Host: Can be written as localhost (data source is on the local machine) or the intranet IP of the host where the data source is located.
Connection Select the access method of the data source. Supports access through IP Address, Gateway, SSH Tunnel three methods. - IP Address: Access the data source through the public network address.
- Gateway: A secure and fast intranet access method provided by NineData, which requires the host where the data source is located to be connected first. For connection methods, please refer to Add Gateway.
- SSH Tunnel: Access the data source through an SSH tunnel.
- IP Address: Access the data source through the public network address.
- SSH Tunnel: Access the data source through an SSH tunnel.
Configuration items when Connection is SSH Tunnel - SSH Host: Enter the public IP or domain name of the server where the target data source is located, as well as the corresponding port number (the default port number for SSH service is 22).
- SSH Authentication Method: Select the SSH authentication method.
- Password: Connect through SSH Username (i.e., the server's login name) and Password (i.e., the server's login password).
- SSH Username: Enter the login username of the server where the target data source is located.
- Password: Enter the login password of the server where the target data source is located.
- Key (recommended): Connect through SSH Username and Key File.
- SSH Username: Enter the login username of the server where the target data source is located.
- Key File: Click Upload to upload the private key file, which is a key file without a suffix. If you have not created one yet, please refer to Generate SSH Tunnel Key File.
- Password: Enter the password set when the key file was generated. If you did not set a password during the key generation process, leave this field blank.
Note: After the SSH configuration is completed, you need to click the Connection Test on the right, there may be the following two results: - Password: Connect through SSH Username (i.e., the server's login name) and Password (i.e., the server's login password).
- Prompt Connection Successfully: Indicates that the SSH Tunnel has been established.
- Prompt error message: Indicates a connection failure, you need to troubleshoot the cause of the error and retry.
- Host: Can be written as localhost (data source is on the local machine) or the intranet IP of the host where the data source is located.
DB Account Enter the login username for PostgreSQL. DB Password Enter the login password for PostgreSQL. client character set Define the character encoding used by the application to generate and parse text data (such as GBK,UTF8), NineData will base this encoding to perform bidirectional transcoding between the application and the database to avoid garbled text during reading and writing.client timezone Define the time zone information of the application, NineData will convert the stored data to the defined time zone when reading date and time fields without time zone information and return it. For example, if your application is located in Shanghai, fill in +08:00.Access Region Select the region closest to the location of your PostgreSQL host to effectively reduce network latency. Environment Choose according to the actual business purpose of the data source, as an environmental identifier for the data source. Default provides PROD and DEV environments, and supports you to create a custom environment.
Note: Under the organization mode, the database environment can also be applied to permission policy management, for example, the default Prod Admin role only supports access to data sources in the PROD environment and cannot access data sources in other environments. For more information, please refer to Manage Roles.Encryption Whether to use SSL encryption to access the data source (default off). If the data source enforces SSL encrypted connections, this switch must be turned on, otherwise the connection will fail.
Click the switch on the right to turn on or off encrypted transmission. Click the > to the left of Encryption to expand detailed configuration.- SSL Options: Supports the following four methods.
- Prefer: Automatically detect the SSL status of the server, if the server has SSL enabled, then connect through SSL first, if the server does not have SSL enabled, then connect through non-SSL.
- Require: Always use SSL to connect to the data source, if the server does not support this method or cannot establish an SSL connection for other reasons, the connection will fail.
- Verify-CA: Upload the CA certificate to verify whether the server's service certificate is issued by a trusted institution to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. At the same time, according to the needs, upload the client user certificate and key to verify your own identity and encrypt the communication with the server.
- Verify-full: On the basis of Verify-CA, check whether the subject of the server certificate (such as the hostname, IP address) matches the actual server being connected to ensure the security of the connection.
- CA Cert: When SSL Options is Verify-CA or Verify-Full, it is required to select, specify the CA certificate to verify the server's certificate.
- Client Certificate (optional): If the server requests a client certificate, you must upload the client certificate to verify your own identity. Client Certificate includes the user certificate (.pem) and key (.pk8).
- Key Password: If the uploaded client key file is password-protected, you need to enter the password here, if not set, leave it blank.
After all configurations are completed, click the Connection Test next to Create Datasource to test whether the data source can be accessed normally. If prompted with Connection Successfully, you can click Create Datasource to complete the addition of the data source. Otherwise, please recheck the connection settings until the connection test is successful.
Appendix: Add NineData's IP address to the PostgreSQL database whitelist
When adding a data source located in On-Premise/Other Cloud, you need to add the IP address of the NineData service to the PostgreSQL database whitelist to allow NineData to provide services.
This section takes PostgreSQL version 10.9 as an example to introduce how to add an IP whitelist.
Open the PostgreSQL configuration file
postgresql.conf, which is usually located at:<PostgreSQL installation directory>/data/postgresql.conf.Find the
listen_addressesparameter, remove the comment (#) symbol in front of it, and set its value to'*'to allow connection requests from all IP addresses, then save and exit thepostgresql.conffile.Open the
pg_hba.confconfiguration file, which is usually located at:<PostgreSQL installation directory>/data/pg_hba.conf.Find the
IPv4 local connectionsorIPv6 local connectionsline, and add the IP address range that needs to be allowed to access below theADDRESScolumn, for example, if you need to allow access from the192.168.1.0 ~ 192.168.1.255address range, configure as shown below.# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
#local all all trust
# IPv4 local connections:
#host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
host all all 192.168.1.0/24 md5Save and exit the
pg_hba.confconfiguration file, then restart the PostgreSQL service to take effect.