Data Source-Level Permission Control
This article demonstrates that after enabling data source-level permission control in a dedicated cluster, users who lack permissions for the target data source will be unable to perform operations on related tasks.
Background Information
In NineData dedicated clusters, once replication tasks are started, users can manage scheduling operations via Operations > Schedule.
In multi-user scenarios, there is a risk of unauthorized operations or mistakes, which can impact production services and cause serious consequences.
To address this, NineData links data source-level permissions with Operations Center task management, ensuring that only users with permissions on the target data source can perform operations on related tasks. This mechanism guarantees:
- Task Visibility: Users can still be aware of the task’s existence and its basic information.
- Operation Isolation: Only users with the appropriate data source permissions can intervene in task execution.
Feature Description
In a NineData dedicated cluster, data source permissions not only determine whether a user can access a given data source, but also directly define the user’s operation scope in task management:
| Permission Status | Task Visible | View Task Details | Modify Task Workflow & Properties | Start/Stop Operations | Login to Terminal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No target data source permission | ✅ Allowed | ✅ Allowed | ❌ Prohibited | ❌ Prohibited | ❌ Prohibited |
| With target data source permission | ✅ Allowed | ✅ Allowed | ✅ Allowed | ✅ Allowed | ✅ Allowed |
The following table explains the authorization subjects and authorization scope for NineData data source permission control:
| Permission Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorization Subjects | Subjects can be either users or roles:
|
| Authorization Scope | Authorization can be based on specific data sources or on environments:
|
Scenario Setup
Replication Tasks: The admin user (
admin) creates two replication pipelines in advance:MySQL A > MySQL B, andMySQL C > MySQL D.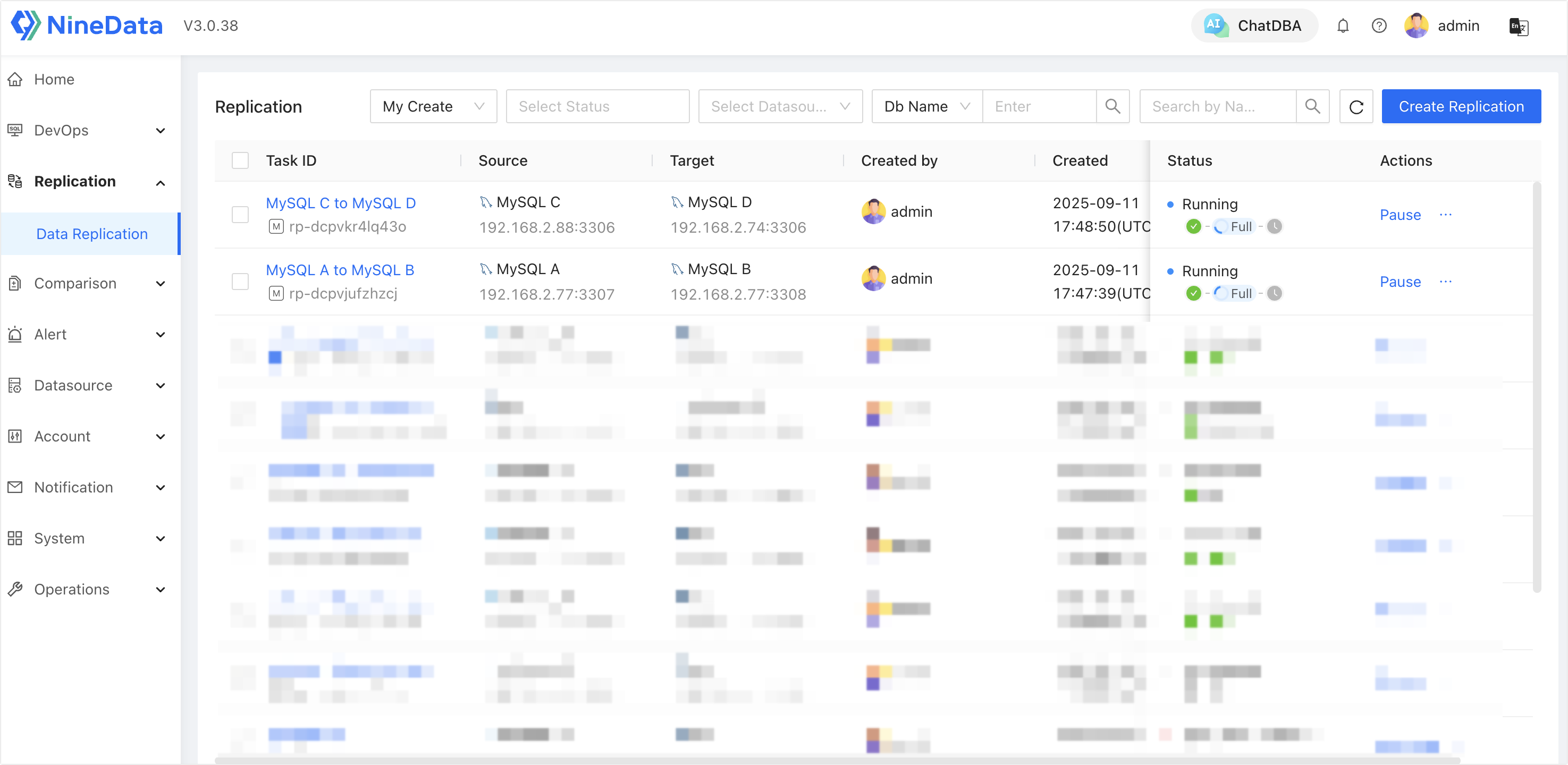
Users: Two different users are created, each granted different data source permissions. Then, log in as each user to perform operations on tasks with and without permissions.
User Role Name Authorized Data Sources user_a role_mysql_a-b MySQL A, MySQL B user_b role_mysql_c-d MySQL C, MySQL D Final result:
user_acannot operate tasks related to MySQL C/D.user_bcannot operate tasks related to MySQL A/B.
Step 1: Create Roles and Configure Data Source Permissions
Log in to the NineData console using a system administrator account.
In the left navigation bar, click Account > Role.
Click Create Role, and create two roles:
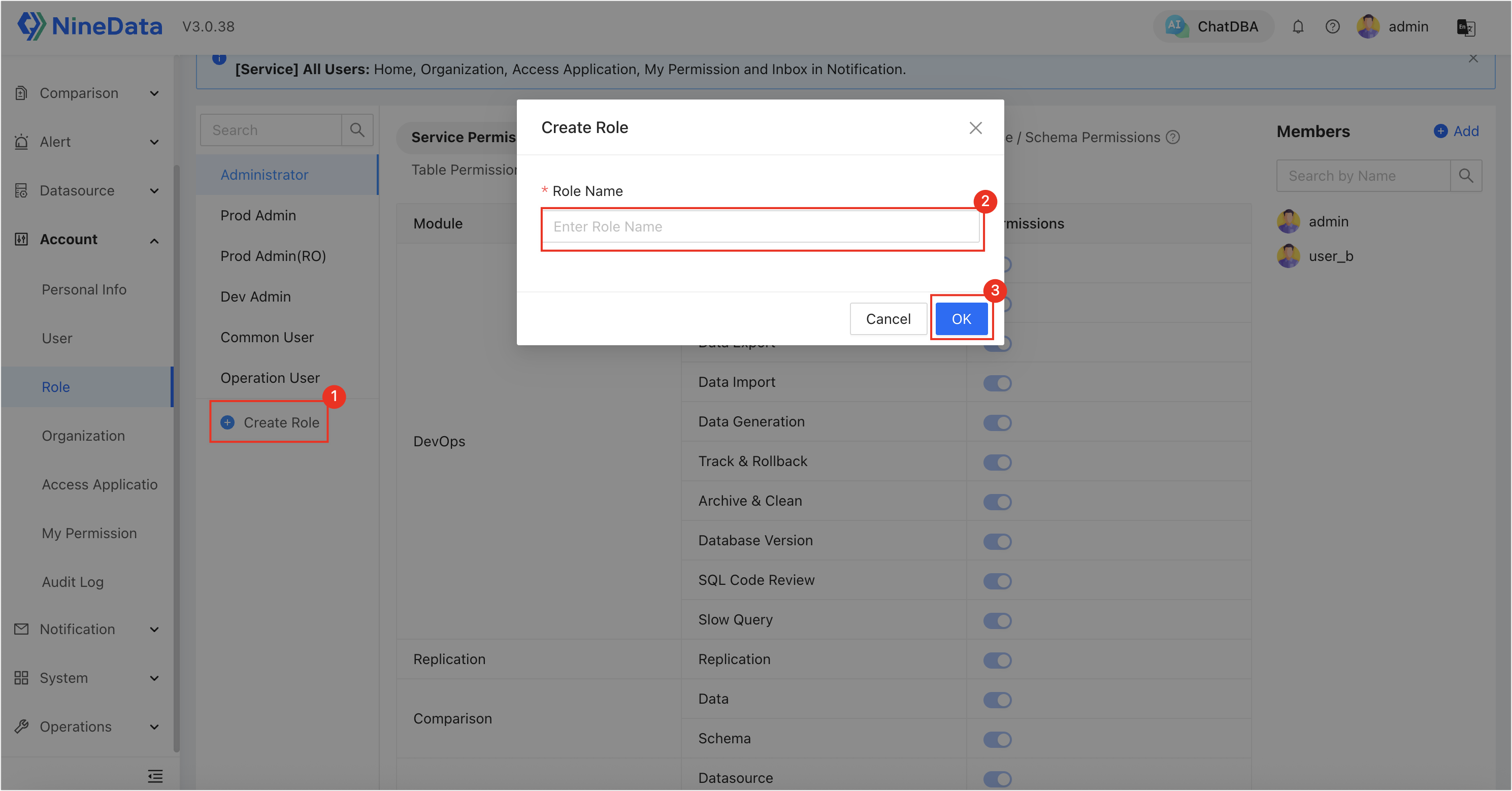
role_mysql_a-brole_mysql_c-d
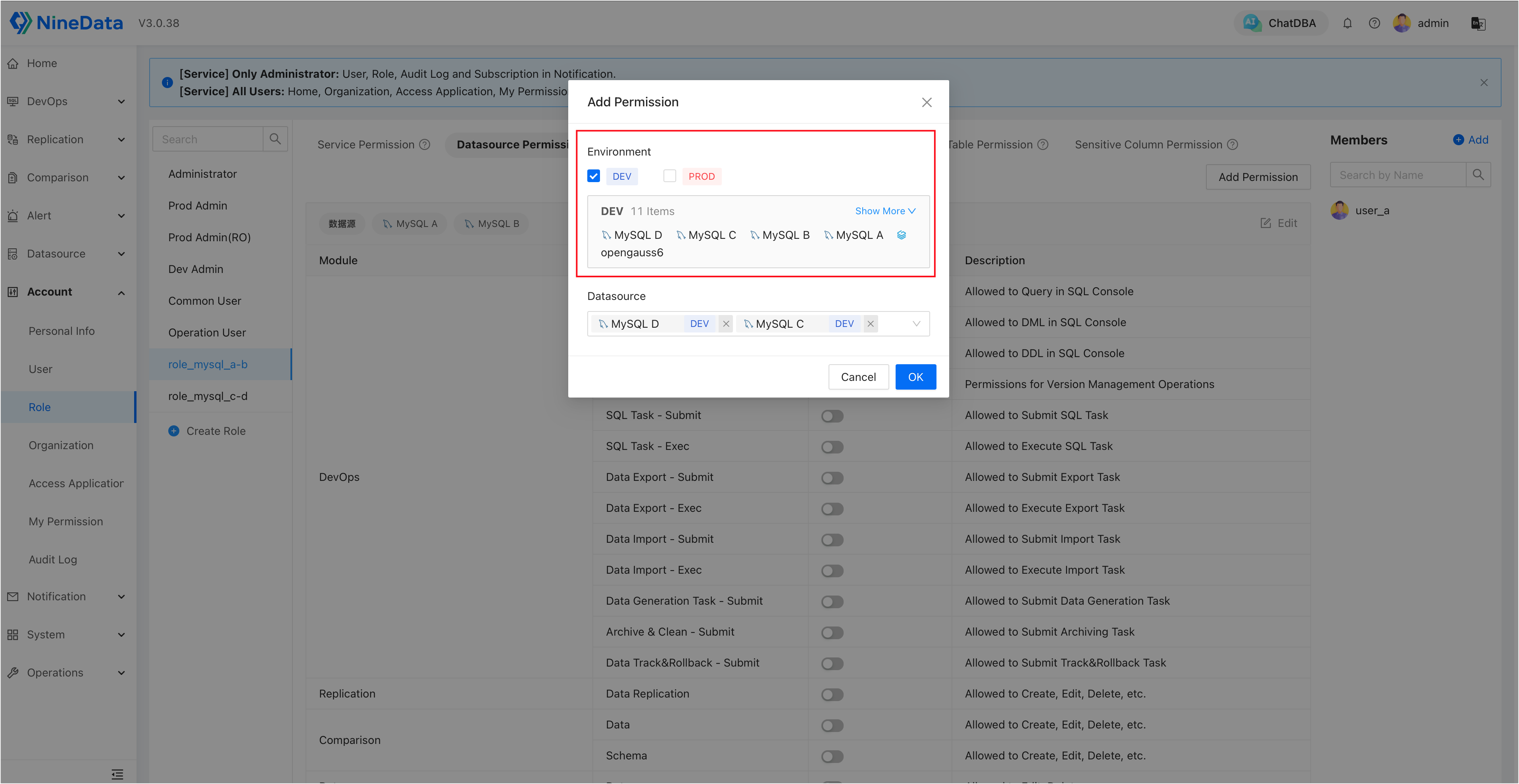
Click on a target role, then go to the Datasource Permission tab and click Add Permission to assign different data source permissions to the roles:
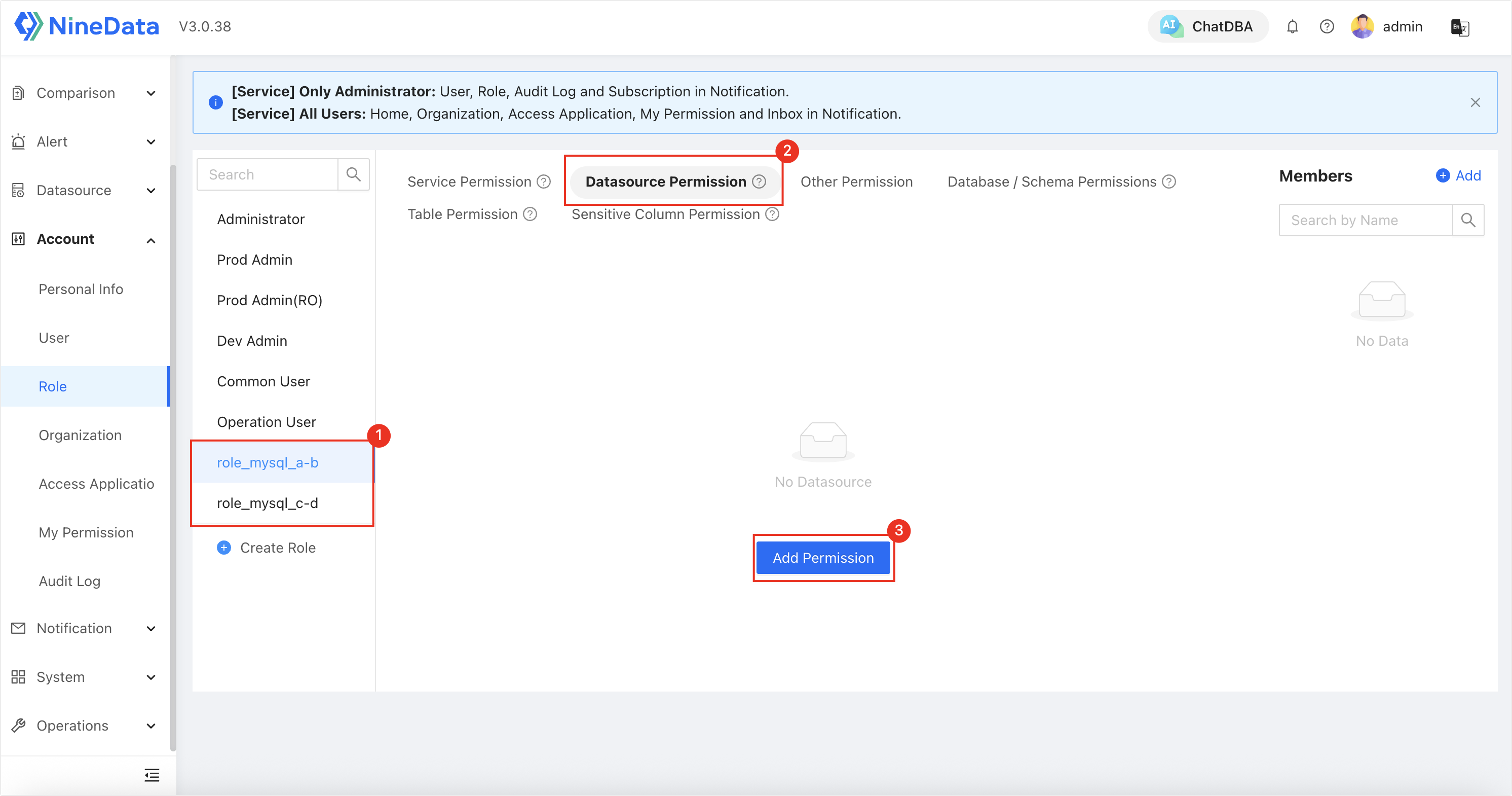
role_mysql_a-b: Authorized to accessMySQL AandMySQL B, and granted Schedule permissions (including Service Permission and Datasource Permission).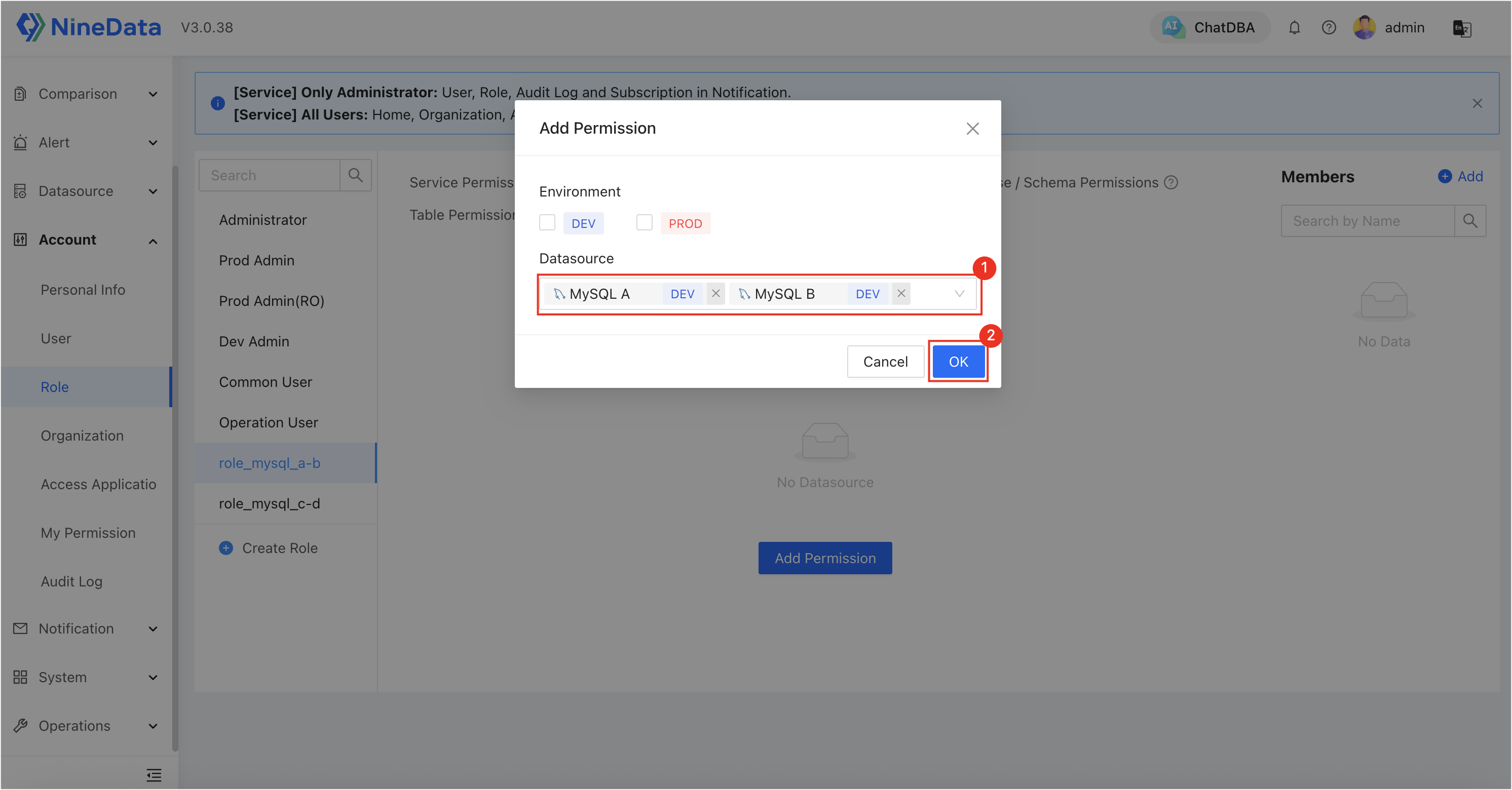
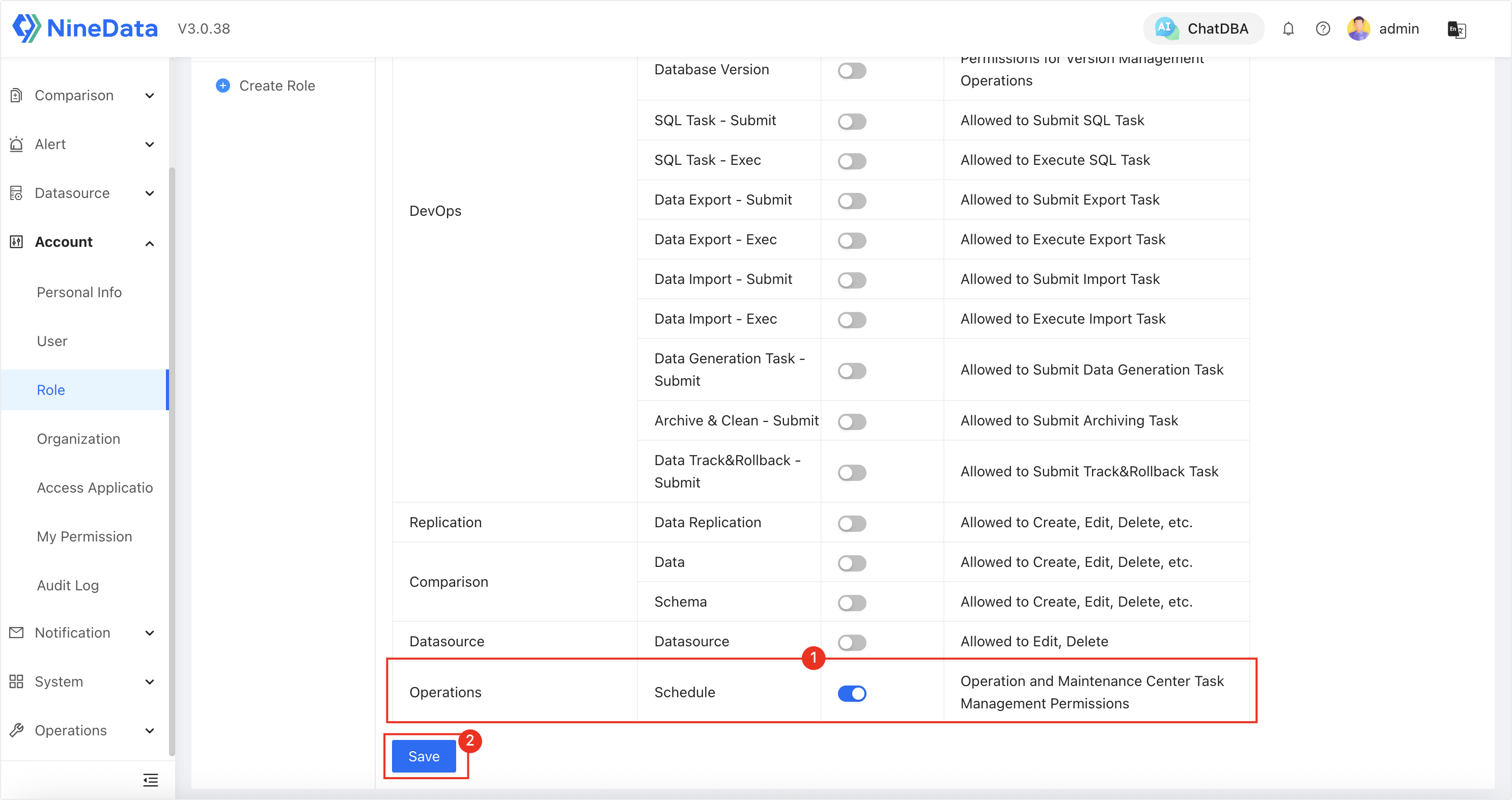
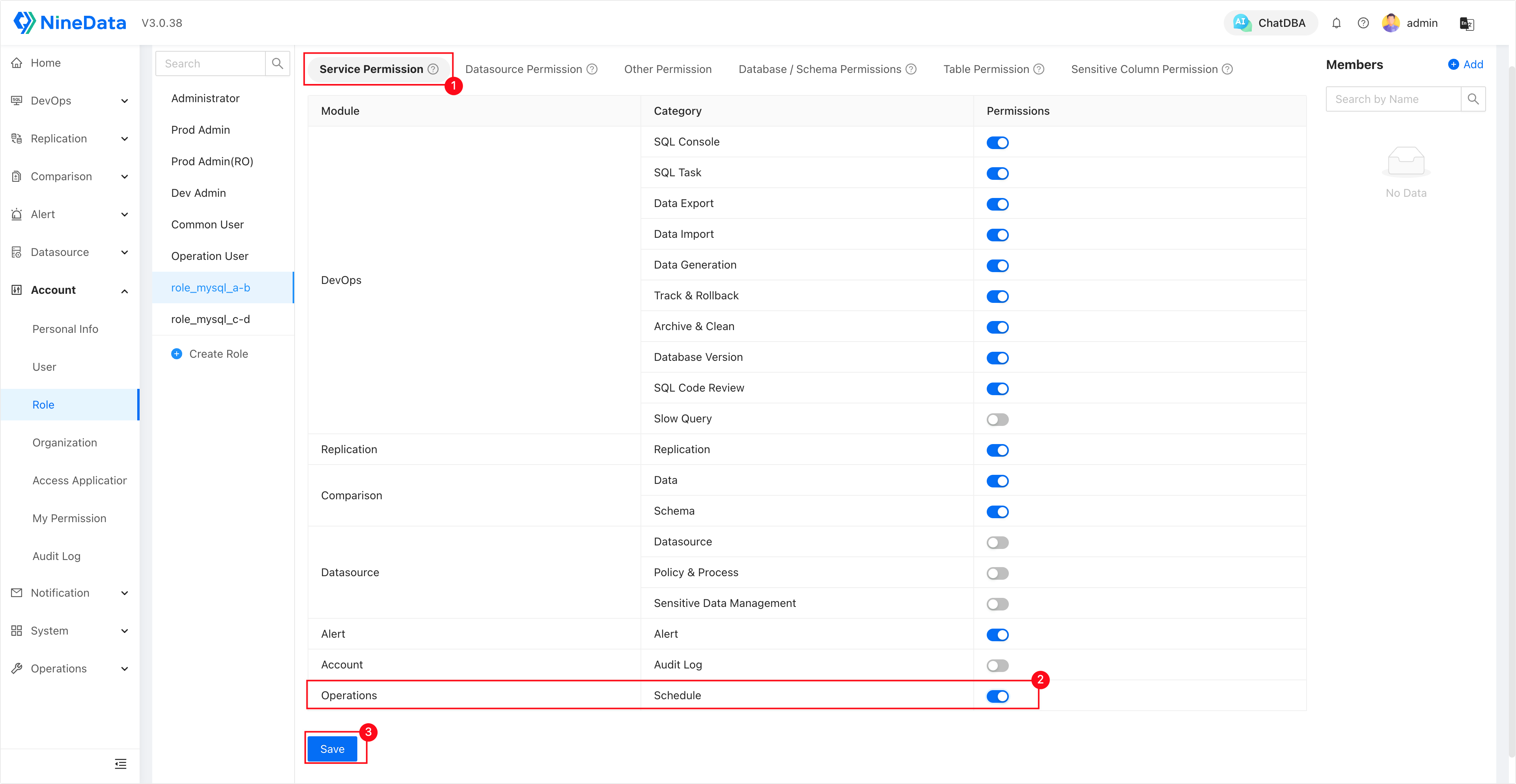
role_mysql_c-d: Authorized to accessMySQL CandMySQL D, other permissions are the same asrole_mysql_a-b.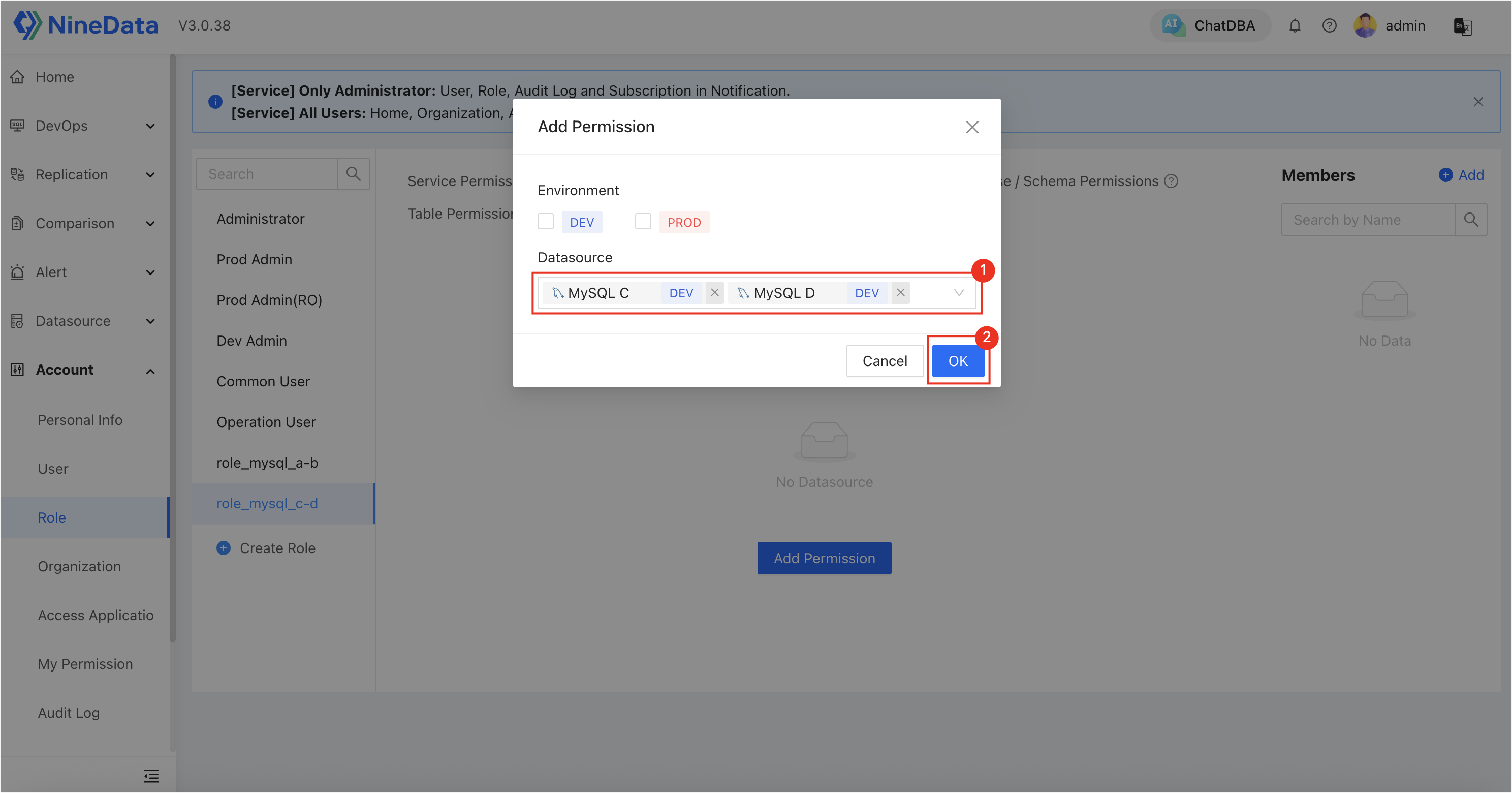
tipIf your data sources are strictly categorized by environment, and you need to grant a role access to all data sources within an environment, you can simply select the environment name under Environment.
Step 2: Create Users and Bind Roles
Log in to the NineData console using a system administrator account.
In the left navigation bar, click Account > User.
In the top-right corner, click Invite, create two users, and bind each to the roles created in Step 1. Click OK, and the system will generate login credentials.
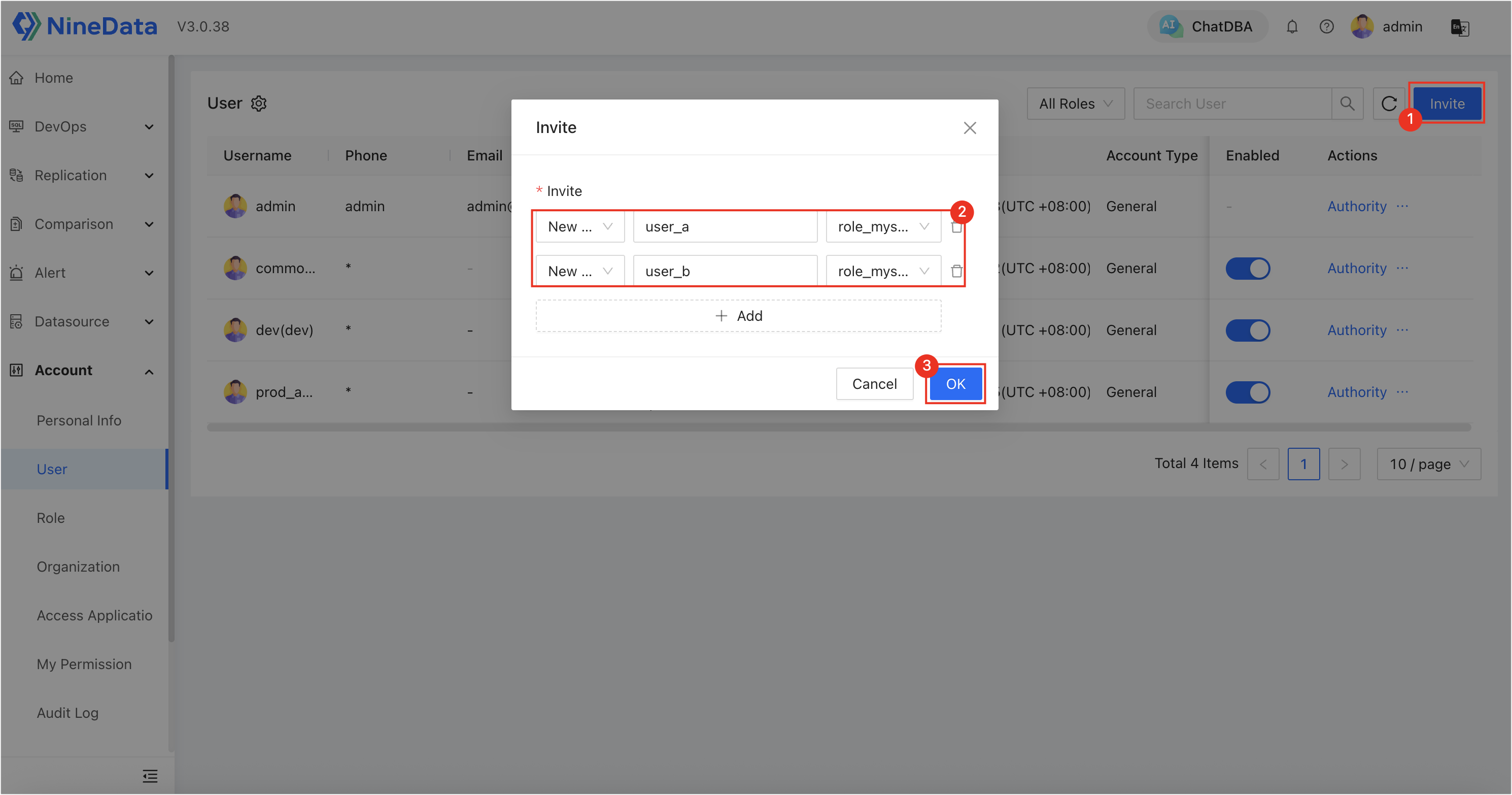
user_a: bound torole_mysql_a-b.user_b: bound torole_mysql_c-d.
Step 3: Use user_a or user_b to View and Attempt Task Operations
Log in to the NineData console with either of the accounts created in Step 1. In this example, log in as
user_a.In the left navigation bar, click Operations > Schedule. On the Task List page, you can see the two replication tasks created by the admin. Among them,
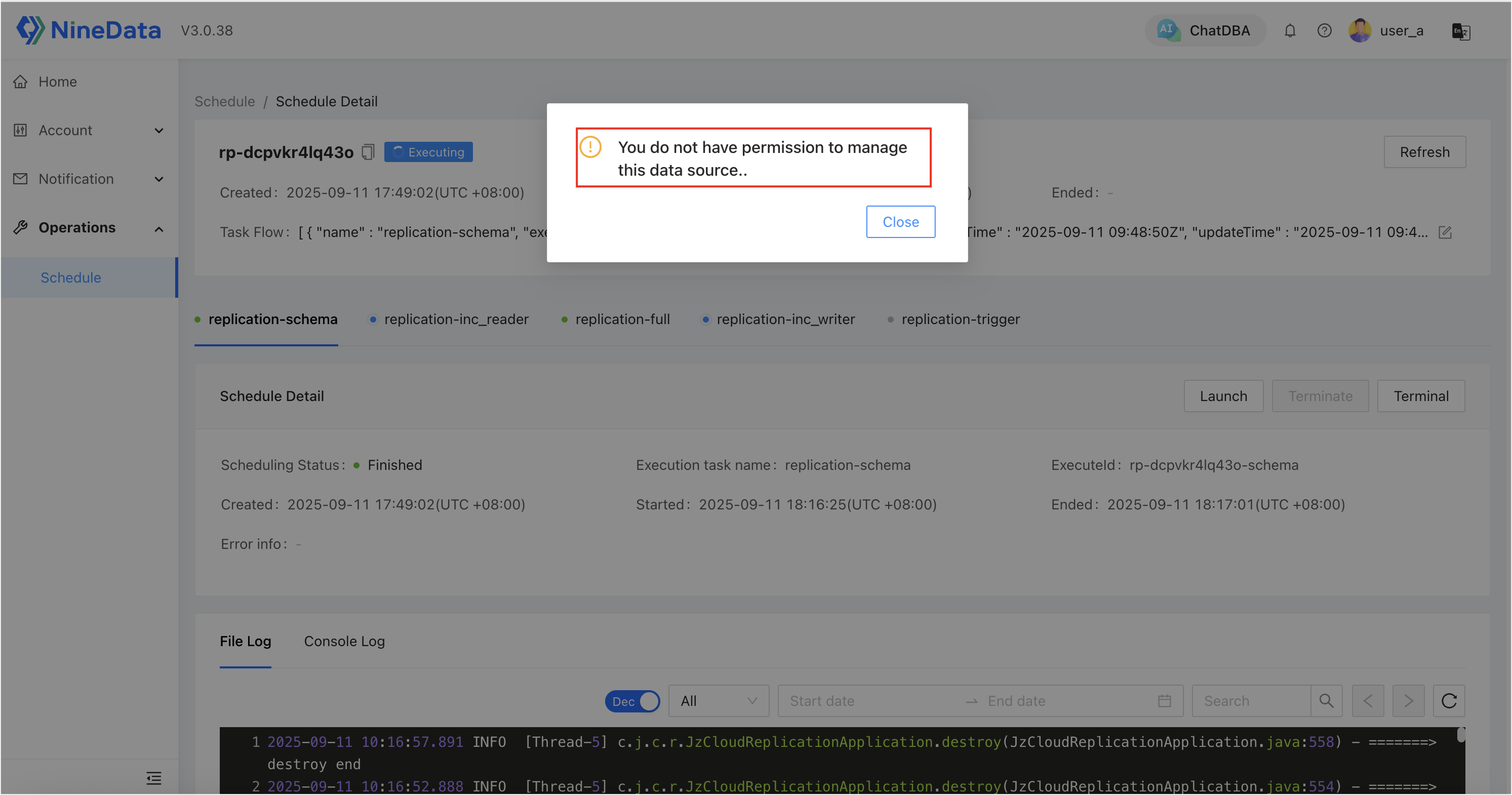
rp-dcpvjufzhzcjis the oneuser_ahas data source permission for.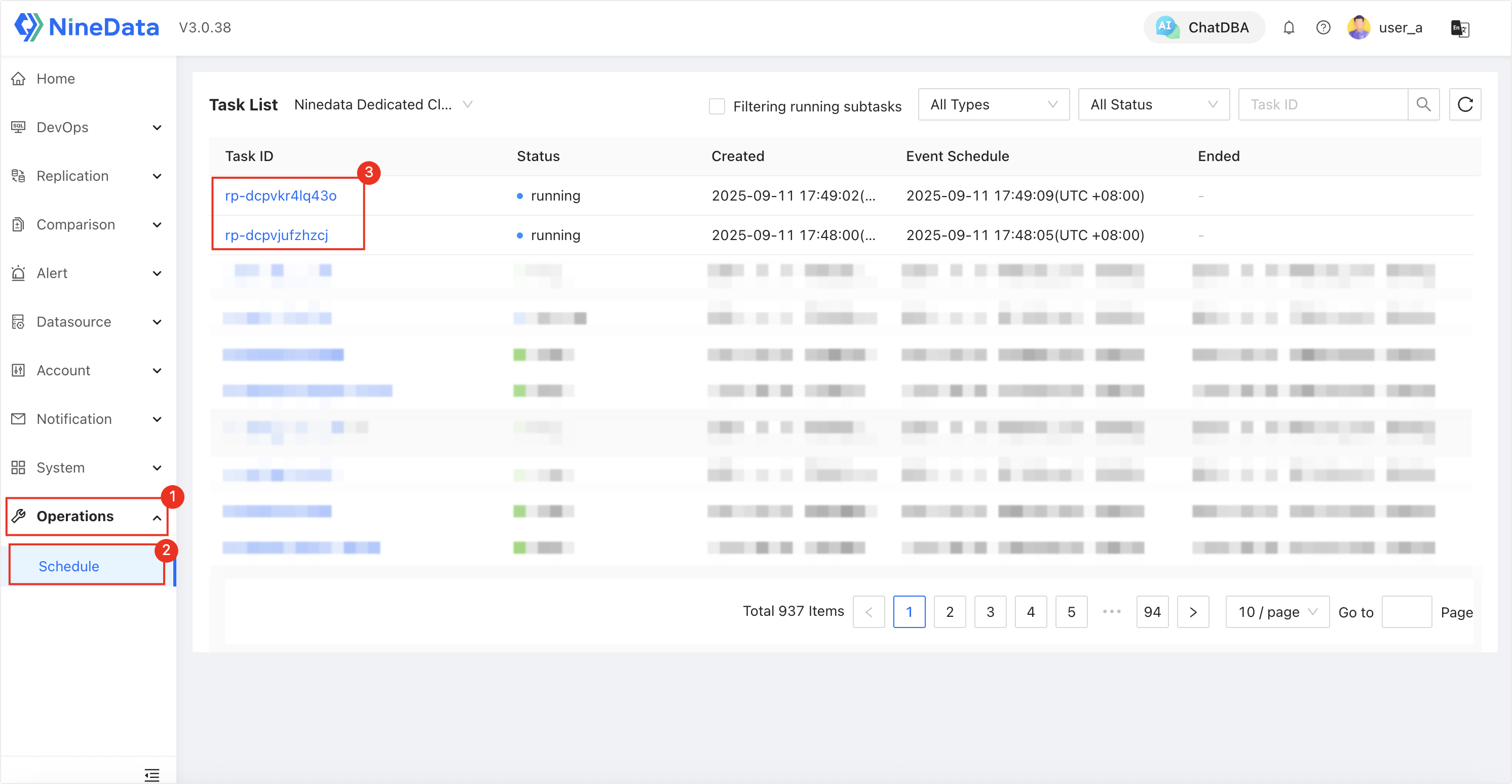
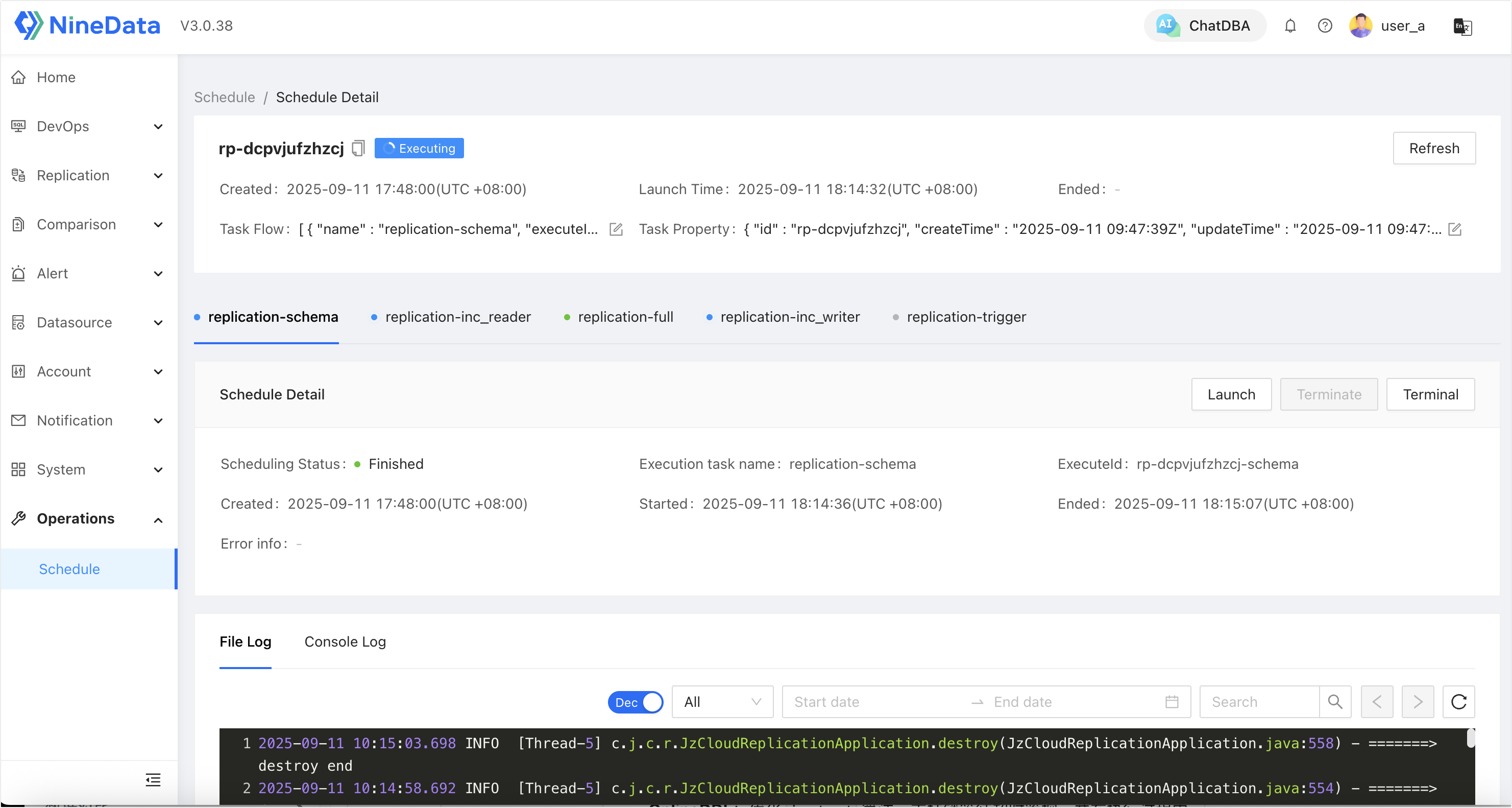
Click on the permitted task ID to enter the details page, where you can view details and perform all available operations.
Go back to the task list page, click on a task ID for which the user has no permission, and enter the details page. The user can view the details but cannot perform any operations, which will display a "no permission" prompt.